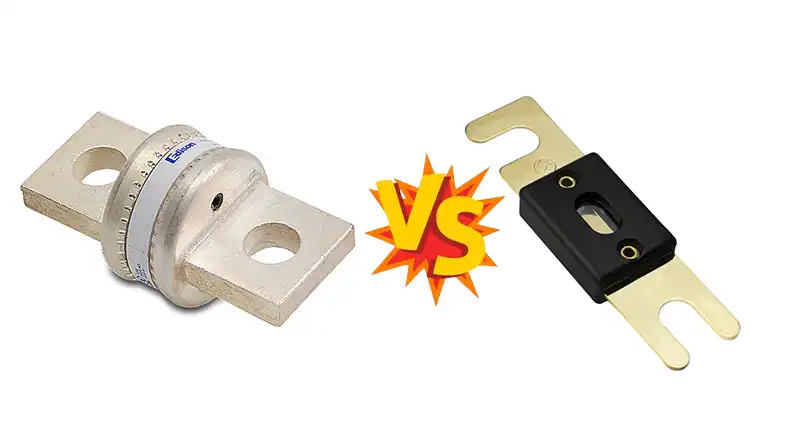
Class T vs ANL Fuse | Key Aspects Compared
The two most common fuse types used in 12, 24, and 36 volt DC systems on boats and RVs are Class T and ANL fuses. While both safely interrupt dangerous electrical faults, they have key differences.
Class T fuses are compact, blade-style fuses that are lower cost and easy to replace. ANL fuses feature rugged, all-nickel construction and higher current ratings, but have a larger size and higher initial cost. Both meet industry standards for DC circuit protection.
Class T and ANL fuse compares physical size, electrical performance, and cost considerations to help determine the best choice of fuse for specific marine and RV DC system applications. The optimal fuse depends on factors like circuit voltage, required amp capacity, and short circuit interruption needs.

Class T Fuses And ANL Fuses
In case of electrical protection, two trusty warriors stand guard: Class T and ANL fuses. While both ensure the safe flow of electricity, they each specialize in different domains.
Class T fuses, with their sleek blade design, excel in lower-voltage systems (12, 24, and 36 volts DC). Think of them as the vigilant sentinels of smaller, more delicate electrical paths. They adhere to the strict UL standard 248-15 for low voltage fuses, ensuring reliable protection within their designated territory.
ANL fuses, on the other hand, embody the bold and resolute. These fast-acting guardians conquer the same voltage battlegrounds (12, 24, and 36 volts DC) but in the rugged landscapes of marine and RV systems. Meeting the demanding SAE J554 and UL standard 248-14, they stand strong against potential surges and high-demand situations.
Choosing the right guardian depends on your electrical kingdom. If smaller circuits require a compact and agile protector, Class T fuses fit the bill. But if your domain pulsates with the raw power of high-demand environments, the unwavering strength of ANL fuses might be your champion.
Remember, both Class T and ANL fuses play essential roles in electrical safety. Choose wisely, and their steadfast protection will ensure the harmonious flow of power within your electrical world.
Comparison Table Between Class T vs ANL Fuse
This table provides a side-by-side comparison of key features and characteristics of Class T and ANL fuses, making it easier to understand the differences between the two types.
| Feature | Class T Fuse | ANL Fuse |
| Definition and Purpose | Designed for high-speed circuits and general-purpose protection. | Used in various applications, including automotive and marine systems. |
| Current Ratings | Typically available in lower current ratings, suitable for electronic devices and small circuits.Example: 30A, 40A, 50A, 60A | Available in a wide range of current ratings, making them versatile.Example: 125A, 150A, 175A, 200A, 250A |
| Voltage Ratings | Moderate voltage ratings suitable for low to moderate voltage applications. | Higher voltage ratings suitable for automotive and industrial use. |
| Time-Current Characteristics | Quick-acting with precise time characteristics, offering precise protection. | Generally quick-acting, providing reliable protection. |
| Physical Size | Compact design, suitable for limited space applications. | Larger physical size, often used in applications with more space. |
| Applications | Commonly used in electronic applications and smaller circuits. | Widely used in automotive, marine, and industrial applications. |
| Advantages | Fast response time, compact design, suitable for high-speed circuits. | Versatile, suitable for various applications, robust construction. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost compared to ANL fuses. | May have a higher cost, especially in higher current ratings. |
| Common Uses | Electronics, small circuits, Telecommunication equipment. | Automotive systems, marineapplications, industrial equipment. |
Key Differences Between Class T and ANL Fuses
You’ll find a clear distinction between Class T and ANL fuses right from the start: their size and design. Class T packs a punch in a compact package, using a blade terminal for a sleek, space-saving fit. ANL, on the other hand, demands more real estate with its hefty stud terminal connectors.
When it comes to electrical performance, their strengths diverge. ANL shines with superior short circuit protection, ideal for high-current demands. It also boasts lower voltage drop, keeping your system humming efficiently. Class T, however, excels in lower current branch circuits, offering the perfect balance of protection and efficiency for smaller, delicate electrical paths.
Finally, there’s the cost factor. Class T’s initial price tag might seem friendlier, but its less robust design could lead to more frequent replacements. ANL, with its higher upfront cost, offers a longer-term investment, potentially saving you money in the long run.
Ultimately, choosing the right fuse depends on your specific needs and priorities. Consider the space you have, the electrical demands of your system, and your budget to find the perfect guardian for your circuits.
Advantages of Class T Fuses
Here are some advantages of Class T fuses given below:
- Slip seamlessly into tight spaces, making them ideal for cramped setups.
- Simple design eases installation and future replacements.
- Cost-effective option compared to some alternatives.
- Works well in various scenarios, from smaller circuits to space-constrained systems.
- Delivers adequate protection for a range of applications.
Remember, while Class T fuses shine in many situations, they may not be the ultimate choice for every system. Consider your specific needs and demands when making your decision.
Advantages of ANL Fuses
ANL fuses aren’t just any guardians; they’re the musclemen of the circuit protection world. Their robust design boasts several advantages that make them ideal for heavy-duty applications:
- When high-wattage circuits demand an unwavering protector, ANL fuses stand tall. Their superior current capacity ensures they can handle the electrical torrent without flinching.
- Efficiency matters, and ANL fuses deliver. Their design minimizes voltage drop, keeping your system humming along at peak performance, without wasting precious energy.
- From scorching deserts to arctic chills, ANL fuses are built to endure. Their sturdy construction stands up to harsh environments, offering reliable protection even in demanding conditions.
People Also Ask (PAA)
1. Which fuse is bigger, Class T or ANL?
ANL fuses are much larger in physical size compared to the more compact Class T blade-type fuses. ANL fuses are typically rated for higher amp capacities.
2. Can I use an ANL fuse in a Class T holder?
No, due to the different terminal designs and larger size, an ANL fuse is not interchangeable with a Class T fuse holder. You should only use the fuse type designed for the installed fuse block.
3. Is a Class T fuse safer for lithium batteries?
Potentially yes, as Class T fuses may provide better protection against overcurrent conditions that can damage sensitive lithium battery banks. Always refer to your battery and inverter manuals.
4. When would I choose an ANL fuse over a Class T?
For high current, main DC circuit protection in systems over 125A. ANL’s superior performance outweighs the higher cost. Or for extreme heat/vibration resistance.
5. Are Class T fuses cheaper than ANL fuses?
Yes, Class T fuses have a significantly lower upfront purchase cost compared to ANL fuses of the same amp rating. However, ANL fuses tend to have a longer working lifespan.
6. Where can I learn more about choosing the right fuse for my system?
Consult ABYC and NMEA electrical standards, read manufacturer fuse guides, or seek advice from a marine/RV electrician or systems designer. Proper fuse selection is key for safe, reliable system protection.
Final Verdict
When choosing between Class T and ANL fuses, consider application and budget. The affordable Class T works well for lower current branch circuits in marine and RV systems. For central, heavy load protection, specify robust ANL fuses, despite higher initial cost. To select the proper fuse type and rating for your system, consult manufacturer specs, ABYC guidelines, and a marine electrician. Following best practices for installation, inspection and replacement helps ensure safe, reliable DC power.




![[Explore] How Often Do Solar Panels Need to Be Replaced?](https://www.itekenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/How-Often-Do-Solar-Panels-Need-to-Be-Replaced-768x428.webp)
