Impact of Hail on Solar Panels | All You Need to Know
Solar panels are susceptible to various kinds of damage, from routine wear and tear to catastrophic weather events. One of the most destructive weather occurrences that can severely impact solar panels is hailstorms.
Luckily, robust protective measures like specially engineered glass, panel tilt orientation, raised panel mounting, and hail guards can mitigate most hail damage.
In this article, I will provide a detailed overview of how hail damages solar modules, quantify risks in hail-prone areas, outline damage prevention best practices, summarize repair and replacement options after hailstorms, and share solar panel hail damage case studies. Let’s safeguard your investment against this impactful peril.
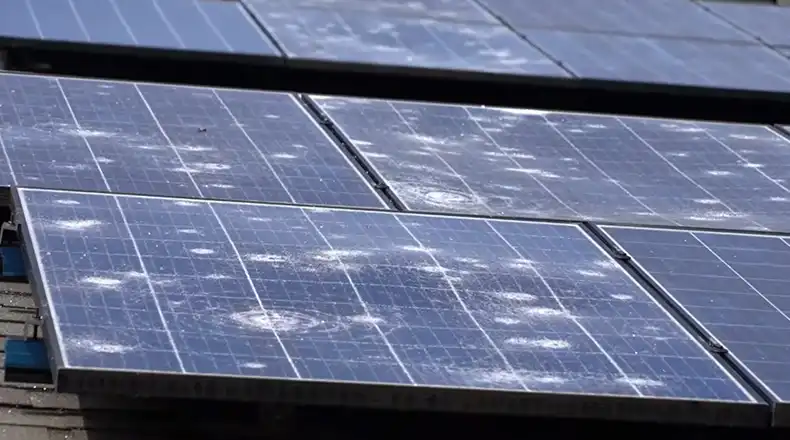

How Hail Damages Solar Panels
Hail can severely damage solar photovoltaic panels in a few key ways:
Cracked Solar Module Glass
Most monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels feature a top layer of specially hardened anti-reflective glass measuring 3.2 to 4 mm thick. When struck by falling hailstones traveling at terminal velocities exceeding 100 km/hr, the kinetic energy can fracture this protective glass casing.

Large hail exceeding 2 cm in diameter poses the highest probability of broken glass. Fractured panels become much less productive as light reflects rather than transmits through to the underlying solar cells. They also become safety risks for fire and electrocution if moisture seeps in.
Damaged Solar Cells and Wiring
If the glass cracks extensively, falling hail can next impact the encapsulated silicon solar cells and copper wiring adhered below the glass. Cells fractured into pieces or deformed from dents will generate far less electricity. Hail- severed internal wiring disrupts power output too.

Dented Aluminum Frames
Most solar panels feature thin anodized aluminum perimeter frames that encompass the laminated glass-cell layers. Hailstones inflict ugly dents that can hamper panel structural integrity over time. But frame damage poses less immediate electrical generation concerns than glass or cell impacts.
Regional Hail Risk Assessments
Solar assets located in hail-prone regions face higher risks of damage over their 25+ year lifespan. The American Meteorological Society analyzed hail patterns across the United States from 2009 to 2018 to quantify high-exposure areas.
Colorado, Nebraska, and Wyoming ranked as the top three states for hailstorm frequency and severity. The Dallas-Fort Worth region documented the highest density of recorded large hail exceeding 2 inches (5 cm) wide.
Referencing location-specific hail data maps can inform protective solar panel measures during design phases. For example, tilting panels at lower angles makes sense for high-latitude solar sites that experience more intense hail. Let’s explore such damage prevention best practices next.
Hail Damage Prevention Measures
While solar panels seem solid, most standard models feature thin glass vulnerable to fracturing. Utilizing the following protective measures greatly enhances durability:
Hail-Resistant Glass
Upgrading to fortified glass engineered to withstand hail, wind pressures, and stagnant loads makes economic sense for new solar installations sited in stormy regions. For example, an innovative product called HailGuard solar panel glass features a proprietary chemical strengthening process.
Field testing simulations using steel ball drop tests showed that solar modules with HailGuard glass sustained over 11 times the impact energy of standard glass before fracturing. This glass cracked at recorded forces over 5400 psi versus just 475 psi with normal glass.
While costing 10-15% more upfront, hail-resistant glass significantly reduces long-term damage risks and downtime losses after extreme weather.
Optimal Panel Tilt Angles
Orienting solar arrays at lower tilt angles helps minimize hail damage. Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) modeled that solar panels tilted at 10-degree angles sustained 40% less hail damage than panels angled at 20 degrees.
Shallow 10-degree tilts increase the likelihood that hail will bounce off rather than perpendicularly strike the glass. Just note that flatter northern hemisphere angles will reduce winter solar harvesting. Every site involves tradeoff considerations.
Raised Panel Mounting Heights
Elevating rooftop or ground-mount solar module mounting frames an extra foot or two helps dissipate hailstone kinetic energies before impact. Taller pole mounts that raise panels higher experience less historically documented damage.
But higher also exposes panels to stronger wind uplift forces. So durable bolted connections and wind load support analytics remain imperative too.
Robust Racking Systems
Well-engineered PV module mounting structures capable of surviving hurricane-force winds will also withstand severe hailstorms. Choose grounded pole mounts secured with helical pier foundations or low-profile ballasted footing mounts for rooftops rather than cheaper roof attachment rails that can disconnect and blow panels away in storms.
Hail Guards
For existing solar rooftops vulnerable to hail, some asset owners elect to install raised mesh hail guard screens above the panels to block falling hail. However, these ventilated steel or polymer shields can add hefty additional wind loads that may overwhelm rooftop load limits if not designed properly. Guards also cast some shading over panels to incrementally reduce output. Each location needs a custom engineering evaluation.
Hail Damage Assessment & Claims Analysis
If a severe hailstorm strikes your solar installation, promptly contact qualified engineers to evaluate damage levels through site inspections, photographic analysis, and thermal imaging. Compile documentation like weather reports and hail size verification for insurance claims.
Homeowners should review policy terms for roof and solar equipment coverage. Rooftop solar and battery storage damage may necessitate distinct claims given the high expense. Business insurance policies treat commercial solar arrays differently too.

Documenting accurate timestamps, locations, damage imagery, and on-site weather data assists insurance appraisers. Be sure to assess electrical safety risks if moisture has compromised any underlying wiring. It often makes sense to claim panels as a total loss even for less severe damage since microcracks degrade output.
Hail Damage Repair & Replacement
Depending on claim approvals and policy coverage amounts, owners of damaged solar arrays weigh the pros and cons of repairing or replacing equipment after impactful hailstorms.
Solar Module Glass Repair
Specialty solar glass repair contractors can fill small cracks and dents in panels with clear adhesives to restore watertight encapsulation. However, underlying solar cell defects still hamper electrical output. So complex repairs seldom restore modules back to their original efficiency.
Full solar panel replacements make better long-term financial sense in most heavy hail damage cases. With ever-improving technology, buying upgraded panels often costs less than 10 years ago too.
Insuring Future Resilience
Rather than merely replacing damaged panels with in-kind models, asset owners can choose upgraded glass, frames, and mounting upgrades to minimize future hail and storm impacts based on location risk data.
Selecting anti-hail glass, durable racking, revised tilt angles, and pole mounting height extensions pays dividends through enhanced durability. Building back better shields investments.
Solar Panel Hail Damage Case Studies
Reviewing delivered costs and downtime impacts across a range of real-world solar hail damage claim scenarios informs wise risk management decisions:
Minor Hail Damage
An Arizona school district’s 1 MW ground-mount solar array endured a spring hailstorm with 2 cm diameter hail reported. Onsite inspection revealed several non-structural glass chip fractures and minor aluminum frame dents across the 2-year-old installation’s 2700 panels.
Facility managers filed an insurance claim that met their $7500 policy deductible level based on replacement cost valuations exceeding $270,000. However, the insurer mandated attempting panel repairs first based on total loss terms. Specialty contractors performed injectable sealant repairs for $120 per panel, restoring the array’s functionality.
Key Takeaway: Cosmetic minor hail damage may not require full replacements.
Major Hail Damage
A Texas semiconductor fab plant’s large rooftop array suffered golf ball-sized hail impacting over 80% of panels during a severe thunderstorm. The site’s insurance adjuster deemed the destruction beyond repair financially and approved the $1.3 million system replacement given the high downtime cost equating to over $13K daily production losses.
Crews dismantled and recycled the mangled panels and rails. Newly upgraded panels with reinforced glass, heavier aluminum frames, and adjustable tilt mounting rails replaced the original installation within 2 weeks. The manufacturer’s production team returned the critical facility to full power just three weeks after disaster struck.
Key Takeaway: Major hail damage often economically justifies complete solar installation replacements.
Conclusion
Hail may seem harmless at first glance, but severe storms can cause catastrophic damage to solar PV projects, degrading power output for decades. Glass fracturing, cell destruction, and aluminum denting add up to six or seven-figure asset losses fast. But sticking to physics-based resilience measures pays off long-term. Opting for durable mounts, robust racking, specialized glass, and strategic tilt angle orientations the first time around proves far cheaper than downtime and restoration later. Heeding local weather patterns and insurance realities allows solar power plants to cost-effectively operate through inevitable hail events over operating lifespans beyond 25 years. What other solar panel hail damage concerns or experiences would you like to share or see addressed? Please leave them in the comments section below! Thanks for reading and stay safe out there during stormy weather events.
Questions Frequently You Asked
- What Is The Most Common Hail Damage?
The most frequent hail damage involves cracked or shattered anti-reflective tempered glass casing solar panels. Fractures degrade power performance.
- Should I Repair Or Replace Hail-Damaged Solar Panels?
For minor hail damage confined to just glass casing chips or frame dents, specialty repairs may restore functionality. But more extensive cell and electrical damage often warrants complete solar array replacements.
- How Much Does It Cost To Replace Hail-Damaged Solar Panels?
Replacing destroyed solar panels, racking, and electrical gear carries steep six or even seven-figure price tags for large-scale photovoltaic power plants. Detailed insurance appraisals help value assets and coverage accurately.
- How Can I Prevent Hail Damage On Solar Panels?
Utilizing durable mounting structures, reinforced glass, strategic tilt angle orientation, pole elevation, and guards where possible are key ways to protect solar arrays from severe hailstorms.






