How Much Does Tilt Angle Affect Solar Panels?
The tilt angle of solar panels plays a crucial role in their efficiency, significantly impacting energy production. Proper tilt angle optimization can increase solar panel output by 10-40%, depending on the location and specific circumstances. In today’s blog post, we’ll explain tilt angles for solar panels, providing practical knowledge and actionable recommendations for maximizing your solar energy system’s performance.
What is Solar Panel Tilt Angle
Solar panel tilt angle refers to the vertical angle at which a solar panel is positioned relative to the ground. This angle directly affects how much sunlight the panel can capture throughout the day and year. The optimal tilt angle varies based on several factors, including geographical location, seasonal changes, and local climate conditions.
For most residential installations in the United States, a tilt angle between 30° and 45° is common. However, the ideal angle can range from 0° (flat) in areas near the equator to over 60° in extreme northern or southern latitudes. Understanding these variations is key to maximizing your solar panel’s energy production.
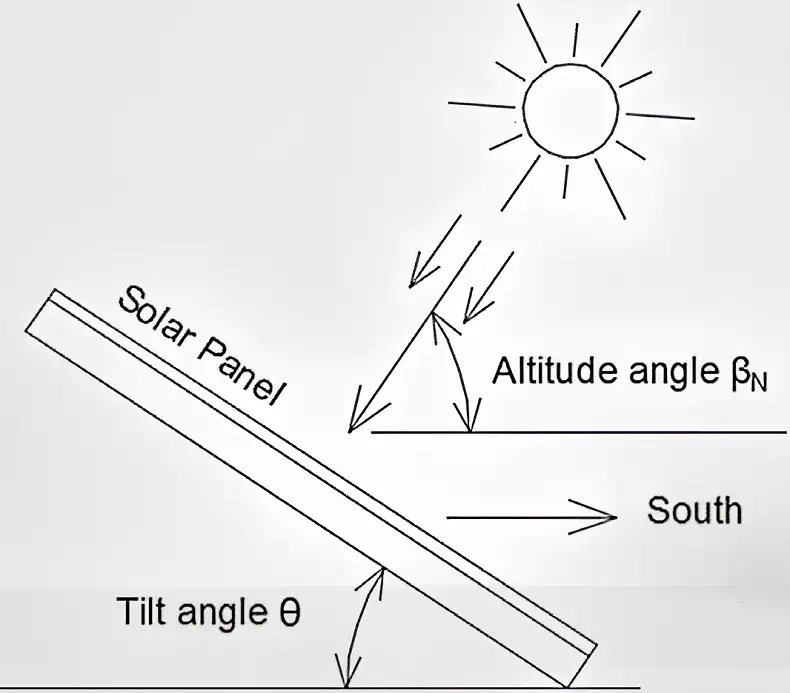
Image: Solar panel tilt angle diagram
Impact of Tilt Angle on Solar Panel Performance
The effect of tilt angle on solar panel performance is substantial. A study conducted by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that optimizing tilt angle can increase annual energy production by up to 40% in some locations. Let’s look at a comparison table to illustrate this impact:
| Location | Optimal Tilt Angle | Energy Production Increase |
| Miami, FL | 25° | 5-10% |
| Denver, CO | 40° | 15-25% |
| Seattle, WA | 30° | 10-20% |
| Anchorage, AK | 50° | 30-40% |
As we can see, the potential for improvement varies significantly based on location. In general, areas farther from the equator benefit more from tilt angle optimization due to the sun’s lower position in the sky.
How Optimal Tilt Angle Is Determined
Now that we know what kind of impact we can expect from the tilt angle, let’s now take a look at how the tilt angle is determined, or rather what affects the tilt angle in different places:
- Latitude: Generally, the optimal tilt angle is close to the location’s latitude. For example, a solar installation in New York City (latitude 40.7°N) would typically have a tilt angle of around 40°.
- Seasonal Variations: The sun’s position changes throughout the year. In the northern hemisphere, a steeper angle (latitude + 15°) works better in winter, while a shallower angle (latitude – 15°) is more efficient in summer.
- Local Climate: Areas with heavy snowfall might benefit from steeper tilt angles to promote snow sliding off the panels. For instance, in snowy regions of Colorado, installers might opt for a 45° to 50° tilt instead of the latitude-based 39°.
- Roof Pitch: For residential installations, the existing roof pitch often dictates the panel angle. While not always optimal, this compromise balances efficiency with installation practicality and aesthetics.
How to Optimize Tilt Angle for Maximum Energy Yield
To optimize your solar panel tilt angle, start by using your location’s latitude as a baseline. For seasonal adjustments, increase the angle by 15° for winter or decrease it by 15° for summer optimization. Consider whether a fixed or adjustable system suits your needs and budget, keeping in mind that fixed systems are simpler but less adaptable.
Utilize online tools like the NREL’s PVWatts Calculator to estimate energy production based on various factors, including tilt angle. Finally, don’t hesitate to consult local solar experts who can provide invaluable insights specific to your area, ensuring you get the most efficient setup for your unique circumstances.
Here’s a simple table to guide your initial tilt angle selection:
| Latitude Range | Recommended Fixed Tilt Angle |
| 0° – 15° | Latitude × 0.87 |
| 15° – 25° | Latitude × 0.76 + 3.1 |
| 25° – 50° | Latitude × 0.76 + 3.1 |
| 50° + | Latitude × 0.615 + 10.5 |
Remember, these are general guidelines. Local conditions and specific system requirements may necessitate adjustments.
Bottom Line
The tilt angle of solar panels significantly impacts their performance, with proper optimization potentially increasing energy production by 10-40%. While the ideal angle varies based on location and specific circumstances, a general rule of thumb is to set the tilt angle equal to your latitude. However, factors like seasonal variations, local climate, and roof structure should also be considered.
By understanding and optimizing your solar panel tilt angle, you can maximize your system’s efficiency, increase your energy savings, and reduce your carbon footprint. Whether you’re installing a new system or looking to improve an existing one, paying attention to tilt angle is a simple yet effective way to get the most out of your solar investment.