Difference Between Solar Cable and Normal Cable | For Your Conveniences
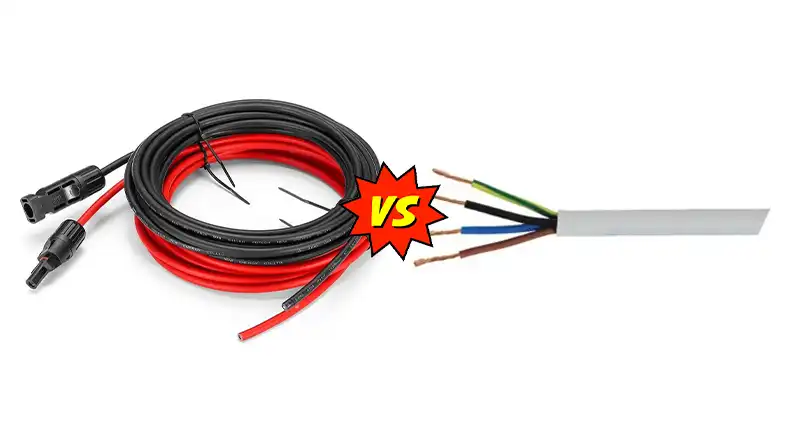
You may already know that solar panel systems require specialized equipment, including specific cables designed for solar applications. This can lead you to wonder – what is the difference between solar cables and normal electrical cables?
Basically, solar cables are engineered to withstand the unique demands of a solar panel system, including extended UV and weather exposure as well as the DC power generated by solar panels. Normal electrical cables lack these specialized properties, making solar cables the proper choice for connecting solar panels and components.
In this article, I will provide an in-depth examination of the key differences between normal electrical cables, specialized solar cables, construction, technical specifications, performance properties, and appropriate uses of each type of cable. So, what are you waiting for, let’s learn them all!
Construction and Design Differences
Solar Cables
Solar cables have a specialized construction that differs from standard electrical wire and cable in several key ways:
- Thicker Insulation: Solar cables feature a thicker layer of insulation than standard electrical wire. This improved insulation protects against UV degradation, cuts down on signal loss, and prevents arcing and fires.
- UV and Weather Resistant Outer Sheathing: The outer sheathing or jacket of solar wire incorporates UV stabilizers and weather-resistant polymers. This protects the cable from prolonged sun and weather exposure when installed outdoors.
- Tinned Copper Strands: Solar wire utilizes tin-coated copper conductors. The tin plating prevents the copper from oxidizing and corroding over time when exposed to weather.
- High-Temperature Resistance: Insulation and sheathing compounds are designed to withstand high temperatures. This prevents melting or cracking, keeping cables safe and functional.
- Flexible Materials: Solar cables use flexible insulating and sheathing materials. This allows the wires to expand and contract without damage as temperatures fluctuate.
- DuPont PV Wire Construction Many solar cables follow a specialized DuPont PV wire construction standard. This includes silver-bearing tinned copper conductors and cross-linked polyethylene insulation.
These design elements equip solar cables to stand up to the demanding conditions of a solar installation. Now let’s look at the technical specifications.
Standard Cable
Standard electrical cable has a simple construction optimized for generic indoor applications:
- Basic PVC or rubber sheathing: The outer sheathing is made from basic PVC or rubber materials. It provides general environmental protection but lacks UV stabilizers for solar use.
- Uncoated copper conductors: Copper wires contain no additional tin plating. This leaves conductors exposed to potential corrosion when used outdoors.
- Generic polyethylene insulation: A thin layer of inexpensive polyethylene typically insulates conductors. This lacks temperature and UV resistance compared to cross-linked solar insulation.
- Limited flexibility: Standard cable can become brittle and rigid when subjected to continuous bending and movement. Solar cables use more flexible compounds.
Overall, standard cable construction lacks weatherproofing and specialized materials to withstand solar system environments, falling short of solar cable engineering.
Differences in Specifications
Solar Cable
Solar cables are engineered to precise technical specifications that enable reliable performance in solar energy systems:
- Voltage Rating – Solar cables have 600-1500V voltage ratings for use with common residential and commercial solar panel configurations.
- DC Current – They are rated for DC power transmission, not standard AC current. This matches the DC output of solar photovoltaic panels.
- Temperature Resistance – Can withstand high temperatures up to 90°C, 140°F or more to prevent heat damage.
- UV Resistance – Formulated to resist damage from ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Tested to thousands of hours of UV exposure.
- Weather Resistance – Sheathing compounds are waterproof and chemical/corrosion resistant for outdoor installation.
- Flexible – Able to handle repeated bending and movement in the wind without breaking down.
- Copper Conductors – Pure copper or tinned copper strands for optimal conductivity.
- Conductor Size – Available in a range of conductor sizes to handle required electrical loads and current.
- Wire Gauge – Common gauges used include 10 AWG, 12 AWG, and 14 AWG for solar applications.
These technical specs enable solar wire to perform reliably in the harsh outdoor environment of a solar installation over decades of use.

Normal Electrical Cables
In contrast to the specialized solar cable, standard electrical wire and power cables are designed for generic indoor applications like wiring a home or building:
- Lower Voltage – Rated for only 300V or less for standard 120/240V AC power transmission.
- AC Current – Designed for indoor use with alternating current, not solar DC current.
- Lower Temperature Rating – Typically rated for only 60-75°C operation.
- Not UV Resistant – Sheathing lacks UV inhibitors, leading to degradation outdoors.
- Less Durable Sheathing – Basic PVC or rubber sheathing lacks weatherproofing.
- Less Flexible – Can become brittle when bent repeatedly.
- Bare Copper Conductors – No tin plating for corrosion protection.
- Standard Wire Gauges – 14 AWG or 12 AWG for lighting and receptacles.
While standard electrical wire works fine for household AC wiring, it lacks the durability, temperature tolerance, UV resistance, and DC rating required for solar installations.
Proper Applications
Solar Cable
Given the demanding needs of outdoor solar systems, solar cables have been engineered for certain applications:
- Connecting Solar Panels
Solar cables are used to interconnect multiple solar panels in strings and arrays to build up solar systems of required wattages. Their flexible nature and durable sheathing allow cables to endure rooftop elements.
- Wire Runs to Inverter
Cables safely transmit DC power from arrays to the central inverter location. High voltage ratings prevent power loss across long distances.
- Inverter to Electrical Panel
Solar cables connect inverter output to the main service panel and utility electrical grid. Their high-temperature ratings are vital near heat-generating inverters.
- General Interconnections
Any outdoor DC wiring for Renewable energy systems should utilize specialized solar cable. This includes low-voltage lighting systems and other auxiliary connections.
Solar wire ensures safe, reliable transmission of DC power across the entire renewable energy system from panels to inverters to electrical panels.
Standard Electrical Cable
Standard copper building wire finds many applications in indoor AC power systems:
- Branch Circuits
Connecting lighting fixtures, receptacles, and appliances to the electrical panel within the interior of a home or building.
- Motor and Equipment Wiring
Powering indoor AC motors, pumps, machinery, and electrical equipment like fans, blowers, and compressors.
- Structure Wiring
General wiring of switches, outlets, junction boxes, and fixtures in walls, ceilings, and basements of structures.
- Low Voltage Control Circuits
Step-down control voltages for HVAC and security systems, alarm systems, lighting controls, and more.
For these types of general-purpose 120/240V AC wiring applications, standard copper building wire is suitable. Any wiring extending outdoors should utilize solar cable.
Key Differences Summary
To summarize the key differences:
| Feature | Solar Cable | Normal Electrical Cable |
| Voltage Rating | 600-1500V DC | 300V or less AC |
| Current Type | DC only | AC only |
| UV Resistance | Yes | No |
| Weatherproof | Yes | No |
| Temperature Rating | 90°C or more | 60-75°C |
| Conductor Material | Tinned copper | Bare copper |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Key Applications | Solar panels, DC circuits | Indoor AC wiring |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Lifespan | 25+ years | 5-10 years outdoors |
| Warranties | Typically 25 years | 1-2 years |
It is these differences in technical specifications and construction that make solar cable the only safe and viable choice for PV panel installations.
Dangers of Using Standard Cable for Solar Systems
Failing to use proper solar cable can lead to multiple dangers:
- Insulation Damage – Standard insulation will degrade, crack, or melt due to heat and UV exposure.
- Conductor Corrosion – Bare copper strands will oxidize, reducing current flow.
- Connection Failure – Damaged cables can loosen or disconnect completely.
- Resistance and Power Loss – Heat and corrosion increase resistance, dropping power.
- Arcing and Fires – Faults can ignite arcs, electrical fires and melt sheathing.
- Shock and Electrocution Risk – Damage leads to exposed live conductors.
- Premature Failure – Cables will fail in just a few years, requiring expensive replacement.
- Invalidation of Warranties – Using the wrong cables may void equipment warranties.
The results can be catastrophic. Only solar-rated cables should ever be used for DC solar panel installations.
Sourcing Quality Solar Cable
When purchasing solar wire, keep the following tips in mind:
- Seek out cables certified to UL 8703 (PV Wire) or UL 4703 (Photovoltaic Wire) standards for proper solar rating.
- Look for cables rated to 600-1500V DC for solar systems.
- Ensure UV-resistant, weatherproof outer sheathing.
- Copper conductors must be tinned for corrosion protection.
- Gauge size should match system voltage drop and current requirements.
- Stick with reputable solar cable manufacturers that warranty their products.
- Consult solar equipment manufacturers for approved cable types for their systems.
Investing in quality solar cables from leading brands ensures electrical safety, reliability, and optimal power production from your solar array.
Solar Cable Cost Considerations
Premium solar cables do come at a higher cost than standard building wire. However, this added investment pays dividends in terms of safety, performance and durability. Over the 25+ year lifespan of a solar system, using properly engineered cables avoids the need for expensive rewiring and repairs down the road. When factored over the system lifecycle, solar cables offer a superior return on investment compared to generic electrical wire.
Summary
Solar power cables are specially engineered for the unique demands of photovoltaic systems. Their robust construction and technical specs equip them to perform safely and reliably in harsh outdoor DC solar applications. Standard indoor AC electrical cables simply lack the proper voltage rating, conductor materials, temperature resistance, UV tolerance, and flexibility required for solar installations. Using the wrong cable can lead to catastrophic electrical hazards, damage, and underperformance. Investing in quality solar-rated cables specifically designed for PV systems ensures electrical safety, optimal power delivery, and decades of reliable operation. Thanks for learning about this critical solar power topic! Please leave a comment below if you have any additional questions.
Related Queries
Q: Can I Use Thhn Wire For Solar Panels?
A: No, THHN wire does not have the necessary UV resistance, temperature rating, or flexibility to be used safely in solar applications. THHN is designed for standard indoor AC wiring only.
Q: What Size Wire Should I Use For Solar Panels?
A: 10 AWG is commonly used for solar panels and runs under 30 feet. For longer runs, 8 AWG may be required to minimize voltage drop. Follow all manufacturer-size recommendations.
Q: Can The Normal Electrical Cable Be Used Outside?
A: No, normal electrical cable will degrade rapidly when exposed to outdoor UV, weather, temperature extremes, and physical damage. Only solar-rated cable should ever be routed outdoors.
Q: Is Copper Or Aluminum Better For Solar Panels?
A: Copper is highly recommended. It has superior conductivity compared to aluminum and is less prone to corrosion and overheating. Most solar cables utilize copper conductors.
Q: Does Wire Size Affect Solar Panel Output?
A: Yes, undersized cables can lead to excessive voltage drop which reduces system power output. Always use properly sized solar cables per equipment guidelines.




![[Explained] What Size Fuse for 3000 Watt Amp for Solar Inverter?](https://www.itekenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/What-Size-Fuse-for-3000-Watt-Amp-for-Solar-Inverter-768x428.webp)