How Many Watts Does It Take to Charge a Golf Cart? How Do I Calculate?
Golf carts have become a staple in communities and recreational areas, and like any electric vehicle, they require charging. But what does it really take to juice up your golf cart? Many cart owners ponder on this, wondering about the exact wattage requirement for a full charge.
Simply put, the watts needed to charge a golf cart usually falls around 600 to 1000 watts. However, this figure can vary based on your cart’s specific battery type and its capacity.
Curious about the math behind that number or how to optimize your charging? Stay with us! In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about golf cart charging, ensuring you’re always powered up and ready to roll.

Calculating the Wattage of a Golf Cart
The formula to calculate watts is simple: Watts = Volts x Amps.
So, if you know the voltage of your golf cart battery and the amperage of your charger, you can calculate the wattage.
For example, if you have a 48V battery (golf cart battery) and a charger that supplies 15 amps, the wattage required would be:
- 48 volts x 15 amps = 720 watts
This means you’d need a power source that can provide at least 720 watts to charge your golf cart.
The Type and Capacity of Golf Cart Battery
Before diving into the wattage, it’s important to understand a bit about the golf cart’s battery:
Battery Types: Golf carts generally use one of two battery types: lead-acid or lithium-ion. Lead-acid batteries are more common, though lithium-ion versions are gaining popularity due to their longer lifespan and efficiency.
Voltage Ranges: Golf carts can have varying voltage ratings, with 36V and 48V being the most common. The higher the voltage, the more power the golf cart can deliver, and typically, the faster it can go.
Factors that Influence Charging Wattage
While the formula gives you a basic idea, there are a few more factors that come into play:
- Battery Capacity: Two golf carts can have the same voltage but different battery capacities, measured in ampere-hours (Ah). A higher capacity battery will store more energy, hence requiring more watts to charge fully.
- State of Discharge: If your battery is only slightly discharged, it won’t need as much energy to charge compared to a completely drained battery.
- Efficiency of the Charger: Not all the power from your charger goes into the battery; some is lost due to inefficiencies in the charger.
- Environmental Factors: Cold temperatures can increase the resistance of the battery, requiring more power to charge. On the flip side, hot temperatures can reduce the efficiency of the charging process.
Practical Tips for Charging
- Always use the charger recommended by your golf cart’s manufacturer. Using a mismatched charger can lead to inefficiencies and even damage your battery.
- Regularly check the water levels (for lead-acid batteries), clean the terminals, and ensure the battery is in good health. A well-maintained battery charges more efficiently.
- While fast charging can be convenient, doing it too often can reduce the lifespan of your battery.
Charging a golf cart isn’t a complex task, but understanding the wattage requirements and factors affecting it can ensure efficient charging. So, next time you’re planning a ride around the course or your community, you’ll know just how much power you need to get going. And remember, take care of that battery, and it’ll take care of your travels! Thanks for riding along with us on this topic, and happy golfing (or cruising)!
FAQ Corner: Answering the Burning Questions
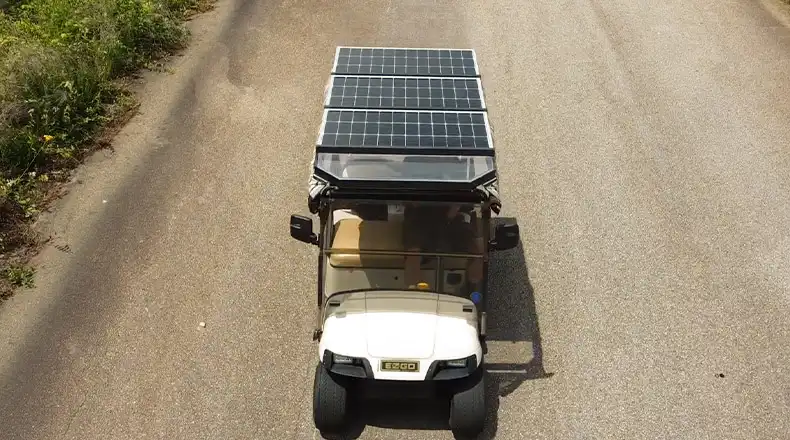
Q: Can I charge my golf cart with solar panels?
A: Yes, many people use solar panels to charge their golf carts, especially if they have a 12V system. It’s eco-friendly and can save on electricity bills.
Q: How long does it take to fully charge a golf cart?
A: Typically, it takes 8-10 hours to fully charge a golf cart. However, this can vary based on the battery’s capacity and its state of discharge.
Q: Is it okay to leave my golf cart plugged in all the time?
A: It’s generally recommended to unplug once the battery is fully charged. Constant charging can lead to overcharging, which can harm the battery over time.