Solar Battery Backup Storage Systems: All You Need To Know

Solar battery backup storage systems are becoming an increasingly popular addition to home solar power setups.
These systems provide a reliable source of power during grid outages, allowing homeowners to keep essential appliances and devices running even when the main electricity supply fails.
By storing excess energy generated by solar panels, battery backup systems offer increased energy independence and can lead to significant cost savings on electricity bills.
Whether you’re looking to enhance an existing solar installation or planning a new system from scratch, understanding the benefits and components of solar battery backup storage is crucial for making an informed decision about your home’s energy future.
What is a Solar Battery Backup System?
A solar battery backup system is an essential component of a comprehensive solar power setup that provides stored energy for use during power outages or when solar panels aren’t generating electricity.
These systems work in conjunction with grid-tied solar installations to ensure a continuous power supply for your home.
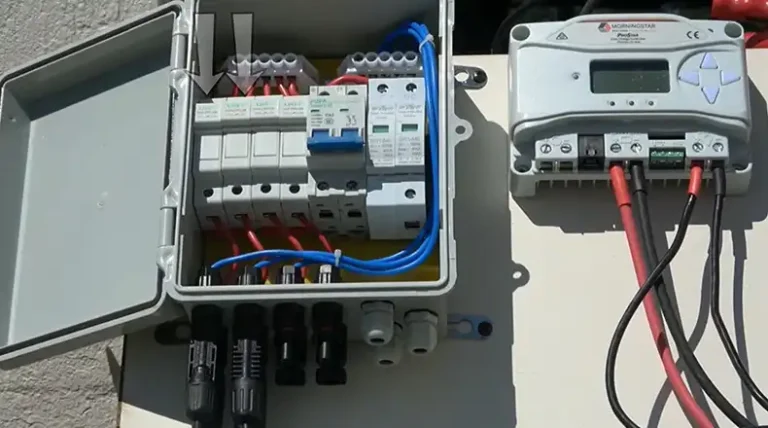
Components Of A Battery Backup System
- Solar panels: The foundation of any solar system, capturing sunlight and converting it into usable electricity.
- Charge controller: Manages the flow of electricity between the solar panels and the battery bank, preventing overcharging and optimizing battery performance.
- Battery bank: Stores excess energy generated by the solar panels for later use. Typically consists of deep-cycle batteries designed for frequent charging and discharging cycles.
- Inverter: Converts the DC power stored in the batteries into AC power that can be used by household appliances and electronics.
- Transfer switch: Automatically switches between grid power and battery power when an outage occurs, ensuring a seamless transition.
How It Works
During normal operation, your solar panels generate electricity that powers your home and feeds excess energy back into the grid. When a power outage occurs, the transfer switch disconnects your home from the grid and switches to battery power.
The inverter then draws power from the batteries to supply your home with electricity until grid power is restored or until the batteries are depleted.
Benefits of Solar Battery Backup Systems
Adding a battery backup to your solar power system offers numerous advantages for homeowners. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
Reliability During Power Outages
One of the primary reasons homeowners invest in solar battery backup systems is to ensure a reliable power supply during grid outages. Whether caused by severe weather, equipment failures, or other factors, power outages can be inconvenient and potentially dangerous. With a battery backup system, you can keep essential appliances and devices running, including:
- Refrigerators and freezers to prevent food spoilage
- Lighting for safety and comfort
- Medical equipment for those with health needs
- Communication devices to stay connected during emergencies
This added layer of energy security provides peace of mind and protection against unexpected power disruptions.
Cost Savings On Electricity Bills
Solar battery backup systems can lead to significant savings on your electricity bills in several ways:
- Time-of-use optimization: By storing excess solar energy during the day, you can use it during peak evening hours when electricity rates are typically higher, reducing your reliance on expensive grid power.
- Reduced grid dependence: With stored energy available, you can minimize your need to draw power from the grid, especially during high-demand periods.
- Net metering benefits: In areas with favorable net metering policies, you can potentially earn credits for excess energy fed back into the grid, further reducing your overall electricity costs.
Environmental Benefits
Incorporating a battery backup system into your solar setup contributes to a cleaner environment:
- Reduced carbon footprint: By relying more on stored solar energy, you decrease your dependence on fossil fuel-generated electricity from the grid.
- Increased renewable energy utilization: Battery storage allows you to make better use of the clean energy your solar panels produce, even when the sun isn’t shining.
- Support for grid stability: By reducing your demand on the grid during peak hours, you help balance overall energy consumption and reduce the need for additional power plants.
Types of Solar Batteries
Choosing the right type of battery for your solar backup system is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Here are the main types of batteries used in solar storage systems:
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have become increasingly popular for solar energy storage due to their numerous advantages:
- High energy density: They can store more energy in a smaller space compared to other battery types.
- Long lifespan: Typically lasting 10-15 years or more with proper maintenance.
- Deep discharge capability: Can be discharged to a greater depth without damaging the battery.
- Low maintenance: Require minimal upkeep compared to other battery types.
- Fast charging: Can be charged and discharged quickly, making them ideal for daily cycling.
However, lithium-ion batteries tend to have a higher upfront cost compared to other options.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have been used in solar systems for many years and come in two main types:
- Flooded lead-acid batteries:
- Lower upfront cost
- Require regular maintenance (water top-ups and equalization)
- Shorter lifespan (5-10 years) compared to lithium-ion
- Sealed lead-acid batteries (AGM and Gel):
- Maintenance-free
- Better performance in extreme temperatures
- Slightly more expensive than flooded lead-acid
- Lifespan of 7-12 years
While lead-acid batteries are generally less expensive initially, they have a shorter lifespan and lower efficiency compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Other Battery Technologies
As the solar storage market evolves, new battery technologies are emerging:
- Flow batteries: Offer long cycle life and can be fully discharged without damage, but are currently more suitable for large-scale applications.
- Sodium-ion batteries: A promising technology that could offer similar performance to lithium-ion batteries at a lower cost, but not yet widely available for residential use.
When selecting a battery type for your solar backup system, consider factors such as initial cost, lifespan, maintenance requirements, and performance characteristics to find the best fit for your needs and budget.
Designing a Solar Battery Backup System
Designing an effective solar battery backup system requires careful consideration of your energy needs and goals. Here’s a guide to help you through the process:
Assessing Your Power Needs
- Identify critical loads: Determine which appliances and devices you want to power during an outage. Common examples include refrigerators, lighting, and communication devices.
- Calculate energy requirements: Estimate the daily energy consumption of your critical loads. This will help determine the battery capacity you need.
- Consider future needs: Factor in potential increases in energy consumption or additional appliances you may want to power in the future.
Choosing The Right Components
- Battery capacity: Select a battery bank with sufficient capacity to meet your energy needs during expected outage durations.
- Inverter size: Ensure your inverter can handle the maximum power draw of your critical loads.
- Solar panel array: If adding panels to an existing system, make sure they’re compatible with your new battery setup.
- Charge controller: Choose a controller that’s compatible with your battery type and can handle the output of your solar array.
Safety Considerations
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation for battery storage areas, especially for lead-acid batteries that can emit gases.
- Temperature control: Many batteries perform best within specific temperature ranges. Consider temperature regulation for your battery storage area.
- Electrical safety: Implement proper grounding and circuit protection measures to prevent electrical hazards.
- Building codes and permits: Familiarize yourself with local regulations and obtain necessary permits before installation.
Installing a Solar Battery Backup System
When it comes to installing your solar battery backup system, you have two main options: professional installation or a DIY approach.
Professional Vs. DIY Installation
Professional installation:
- Ensures proper system design and component selection
- Guarantees compliance with local codes and regulations
- Often includes warranties and ongoing support
- Can be more expensive but reduces risk of errors
DIY installation:
- Can be more cost-effective
- Allows for greater customization and hands-on learning
- Requires significant technical knowledge and skills
- May void warranties if not done correctly
For most homeowners, professional installation is recommended due to the complexity of solar battery systems and the potential safety risks involved.
Retrofitting Existing Solar Systems
If you already have a grid-tied solar system, you can often retrofit it with battery backup capabilities:
- AC coupling: This method involves adding a battery-based inverter to your existing system. It’s generally simpler and less expensive but may be less efficient.
- DC coupling: This approach requires replacing your existing inverter with a hybrid inverter that can manage both solar panels and batteries. It’s typically more efficient but can be more complex and costly to implement.
When retrofitting, consult with a solar professional to determine the best approach for your specific system and needs.
Maintaining Your Solar Battery Backup System
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your solar battery backup system.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Battery maintenance:
- For flooded lead-acid batteries: Check water levels monthly and top up as needed
- For all battery types: Keep terminals clean and free of corrosion
- Monitor battery temperature and ensure proper ventilation
- System checks:
- Inspect wiring connections periodically for signs of wear or damage
- Clean solar panels to maintain optimal efficiency
- Test your system regularly to ensure it functions correctly during outages
- Software updates: Keep inverter and monitoring system software up to date for optimal performance and security.
Maximizing Battery Lifespan
- Avoid deep discharges: Try not to regularly discharge your batteries below their recommended depth of discharge.
- Maintain proper charge levels: Keep batteries at their optimal charge level when not in use.
- Temperature control: Protect batteries from extreme temperatures, which can reduce their lifespan.
- Regular cycling: For some battery types, regular use can help maintain their capacity and overall health.
Cost Considerations
Understanding the costs associated with solar battery backup systems is essential for making an informed decision.
Initial Investment
The upfront cost of a solar battery backup system can vary widely depending on factors such as:
- Battery type and capacity
- Inverter and other component quality
- Installation complexity
- Whether you’re adding to an existing system or starting from scratch
On average, residential solar battery systems can range from $5,000 to $15,000 or more, depending on size and features.
Long-Term Savings And ROI
While the initial investment may seem high, consider the long-term benefits:
- Reduced electricity bills through better utilization of solar energy
- Potential savings from avoiding food spoilage during outages
- Increased property value
- Possible tax incentives or rebates (check local and federal programs)
Calculate your potential return on investment (ROI) by estimating energy savings over the system’s lifespan and comparing it to the initial cost.
Conclusion
Solar battery backup storage systems offer a powerful solution for homeowners looking to enhance their energy independence, reduce electricity costs, and ensure reliable power during outages.
By understanding the components, benefits, and considerations involved in choosing and installing a battery backup system, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your energy needs and goals.
Whether you’re adding storage to an existing solar setup or planning a new installation, the combination of solar panels and battery storage represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Solar With Battery Storage Worth It?
Generally, solar with battery storage is worth it, especially for homeowners looking to maximize their energy independence and savings. It allows you to store excess solar energy for use during peak hours or power outages, reducing reliance on the grid and providing long-term financial benefits.
What Is The Average Cost Of A Solar Backup Battery?
The average cost of a solar backup battery ranges from $6,000 to $13,000. This price can vary based on the battery’s capacity, brand, installation fees, and any additional features.
How Many Solar Batteries Are Needed To Power A House?
Typically, between one and three solar batteries are needed to power a house, depending on the household’s energy consumption, the battery’s capacity, and the amount of energy generated by the solar panels.
How Much Does A 10KW Battery Cost?
A 10kW battery usually costs between $10,000 and $13,000. This cost includes the battery itself and often the installation fees, although prices can vary based on brand and additional features.
How Long Will A 10KW Battery Last?
A 10kW battery will generally last between 10 to 12 hours, depending on the household’s energy usage and the specific conditions of its operation. This duration provides ample backup during nighttime or power outages.