Does a Solar Inverter Need to Be Grounded? Let’s Find Out
Solar panel systems come with their own set of equipment that must be properly installed and maintained. One of the most critical components is the solar inverter, which converts the DC power from the solar panels into usable AC power for your home. However, there is often confusion about whether solar inverters need to be grounded.
In short, yes, proper grounding is absolutely essential for all solar inverters. Grounding provides a safe path for electricity to flow to the ground in the event of a malfunction, protecting you and your home. Without proper grounding, you risk serious hazards from electric shocks, fires, and equipment damage.

In this guide, I have explained why proper solar inverter grounding is so important. Also, I have discussed the following things –
- The National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements,
- Different grounding methods,
- Considerations for grid-tied vs off-grid systems, and
- Steps you can take to ensure your solar inverter is grounded safely.
I hope you’ll find this article informative and useful in the end.
Why Do Solar Inverters Need to Be Grounded?
Grounding solar inverters is about both safety and performance. Here are some of the key reasons why proper grounding is so essential:
- Lightning and Surge Protection
One of the primary purposes of grounding is to protect solar equipment from lightning strikes and power surges. Without a grounding path, a lightning strike could damage your inverter or even create dangerous electric shock risks. Grounding provides a safe path for the electricity to flow to the ground.
- Equipment and Circuit Protection
Grounding also protects the solar inverter and other equipment like batteries from abnormal power flows in the system. If a circuit fault or malfunction occurs, grounding provides a path to divert the excess power away from your equipment and safely dissipate it. This prevents long-term damage to the system.
- Fire Prevention
Improper grounding can lead to potential fire hazards as well. Electricity from malfunctions needs an escape path. Without proper grounding, defects could arc and spark within the electrical system, leading to fires. Proper grounding dissipates the energy safely.
- Shock Hazard Prevention
One of the most dangerous risks from improper solar inverter grounding is electric shock. Without a grounding path, a malfunction could electrify the system components and pose a serious risk of shock to anyone coming in contact. Properly grounding the inverter ensures there is always a safe path for the power to flow to Earth. This protects both you and your loved ones.
- Manufacturer Requirements
Nearly all solar inverter manufacturers require proper grounding to maintain their equipment warranties. Grounding is essential to their safe operation. Without it, any problems resulting from surges or malfunctions would not be covered.
Not grounding your solar inverter puts your entire solar system, home, and personal safety at serious risk. Following the proper grounding guidelines is a must.
National Electrical Code (NEC) Grounding Requirements
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is the primary guidance for all electrical installations in the United States. Here are some key grounding-related requirements from the NEC that apply to solar inverters:
- NEC 690.41 – Requires that the PV array frame and any exposed metal equipment like inverters must be properly grounded. This prevents shock and fire hazards.
- NEC 690.43 – States that grounding conductors for solar systems must be sized appropriately for the inverter output circuit current and should never be smaller than #6 AWG copper wire.
- NEC 690.46 – Requires proper labeling of all grounding connections in the solar system at the point of connection. This helps identify the grounding flow.
- NEC 690.47 – Specifies that any exposed non-current-carrying metal parts of the PV system must be properly bonded and grounded to prevent shock hazards.
- NEC 250.28 – Details proper sizing of grounding electrode conductors and what materials can be used based on the size of the electrical service.
- NEC 250.50 – Covers proper bonding of grounding electrodes made of different metals to ensure continuity between them.
Always check your local electrical code for any additional grounding needs beyond the NEC. However, following these guidelines provides a safe baseline for proper solar inverter grounding.
Grounding Methods for Grid-Tied Solar Inverters
For grid-tied solar systems that operate in parallel with the utility grid, there are two main grounding methods to choose from:
Method 1: Neutral-to-Ground Bonding
This method bonds the neutral output conductor from the solar inverter to the grounding electrode system at only one point. This is usually done at the main electrical service panel and is common when using a transformerless inverter design. It avoids any issues with unexpected ground fault currents.
Method 2: No Neutral-to-Ground Bonding
The second option is to keep the neutral output completely isolated from the ground in the entire system. This avoids any path for electricity to flow and mitigates issues like ground faults. However, it requires careful coordination of ground fault protection systems.
Both methods are compliant with NEC guidelines when done properly. Consulting a qualified solar installer is the best way to determine which grounding approach is right for your specific grid-tied solar system.
Considerations for Off-Grid Solar Inverters
Off-grid solar systems operating independently from the utility grid have some unique grounding considerations:
- Flexibility in grounding locations – Grounding can be done at the inverter, battery bank, PV array frame, or any other single point. Multiple ground rods are often used.
- No bonding of neutral and ground – Keeping neutral and ground isolated is recommended for most off-grid installs for better surge protection.
- Inverter may have a grounded or ungrounded output – Some off-grid power centers have a grounded AC output for use with sensitive loads. Others are left floating for flexibility.
- Lightning protection is critical – Proper surge suppressors and arrestors should be used due to greater lightning exposure.
Consult with your solar designer to evaluate the best grounding solutions for your unique off-grid solar configuration and installation location.
4 Steps to Properly Ground Your Solar Inverter
Follow these key steps to ensure proper grounding that meets NEC requirements:
Step 1: Run a Properly Sized Grounding Electrode Conductor
The grounding conductor between the inverter and the grounding electrode system should be #6 AWG or larger bare copper wire. NEC 690.43 specifies the minimum size based on your inverter output circuit current.
Step 2: Connect to Grounding Electrodes
Bond the grounding conductor to suitable grounding electrodes like ground rods, a concrete-encased electrode, or a ground ring. Use corrosion-resistant clamps.
Step 3: Establish Continuity
Ensure all grounding points are bonded together to establish good continuity by inspecting connections and using properly sized bonding jumpers between different electrode types per NEC 250.50.
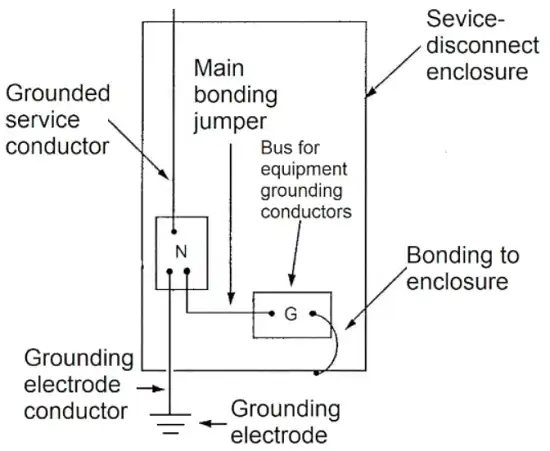
Step 4: Label All Connections
Clearly label all grounding connections with “GND” markings according to NEC 690.46. This identifies the vital grounding path.
Following these best practices for grounding your solar inverter will provide lasting protection for your investment. Never hesitate to contact a qualified electrician if you have any doubts or need assistance in properly meeting code requirements. Your safety is most important.
People Also Asked
Where Should The Inverter Be Grounded?
The solar inverter ground wire should be connected to the main grounding electrode system used by the home, typically at the main electrical service panel. This bonds the inverter ground with other grounds in the home into a contiguous, low-impedance grounding network. For grid-tied systems, ground at the main electrical panel. For off-grid systems, ground at the inverter, battery bank, or any single point in general. Use multiple ground rods spread out.
Does Inverter Need Separate Grounding From Home?
No, the inverter grounding conductor should be bonded to the home’s existing grounding electrode system. No need to drive new ground rods only for the inverter. Utilize the existing grounding infrastructure.
Can I Use The Same Grounding Wires For Solar Panels And Inverter?
Yes, the grounding conductor from the PV array can be bonded to the inverter grounding conductor to use the same path back to the grounding electrode system. Follow proper wire sizing.
What Size Grounding Wire For a 5 KW Inverter?
For a 5 kW inverter, use a minimum #6 AWG copper grounding electrode conductor according to NEC 690.43. Larger is acceptable and preferred for redundancy. Confirm wire gauge meets local codes.
What Is The Main Purpose Of Grounding A Solar Inverter?
The main purpose of grounding a solar inverter is to protect the equipment and ensure safety. Grounding provides a path for stray electrical energy to safely dissipate into the earth in the event of a surge, short circuit, or other malfunction in the solar system. Proper grounding prevents damage to the system and risks of electric shock, fires, and more.
Is It Okay To Ground The Solar Inverter To The Frame Of The Solar Panels?
No, it is not advisable to only ground the inverter to the solar panel frame. The inverter must have a proper equipment grounding conductor running to establish grounding electrodes protected from physical damage. A bond should also be made between the inverter ground and the solar panel frame ground.
What Size Grounding Wire Do I Need For A 7kw Solar Inverter?
For a 7kW inverter, the NEC recommends a minimum #6 AWG copper grounding electrode conductor. However, most installers prefer to use an even thicker wire for a 7kW inverter, with #4 AWG or #2 AWG being common. Check local building codes for the required ground wire size.
Can I Use The Same Ground Rod For My Main Electrical Panel And Solar Inverter?
Yes, you can and should bond the solar inverter ground to the existing ground rods used for the main electrical service panel grounding electrode system. No need to install dedicated ground rods just for the inverter. Ensure proper wire sizing when tying the grounds together.
Summary
Installing solar power systems comes with a great responsibility to follow safety best practices like proper solar inverter grounding. While grounding methods may vary between grid-tied and off-grid systems, the importance of creating a safe path for stray electrical energy to dissipate is universal. Take the time to educate yourself on NEC grounding requirements and work with experienced solar professionals to ensure optimal protection of your investment. With proper grounding, you can power your home with renewable energy from the sun, safely and reliably for decades to come. The comfort and satisfaction of an efficiently grounded system are well worth the effort. Wishing you many bright days ahead with your solar installation! Please leave a comment below if you have any additional questions.