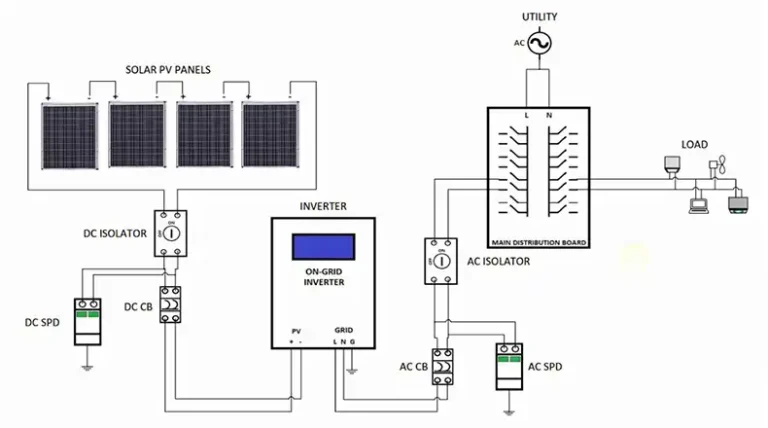
How To Choose The Best Solar Panel System For Your Home?

Choosing the right solar panel system for your home is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your energy savings and environmental footprint.
With numerous options available in the market, it’s essential to understand the key factors that influence your choice.
The most important consideration when selecting solar panels is to determine your specific energy needs and match them with the appropriate system size and panel efficiency.
By calculating your daily energy usage and considering factors like roof space, sunlight exposure, and budget, you can narrow down the options to find the best solar panels for your home.
This guide will take you through the essential steps to help you make an informed decision, ensuring that your investment in solar energy pays off in the long run.
1. Understanding Solar Panel Types
Selecting the right type of solar panel is the first step in your decision-making process. Different types of panels offer varying levels of efficiency, cost, and suitability for different roof types. Let’s dive into the three main types of solar panels available for residential use.
Monocrystalline Panels
Monocrystalline panels are made from a single crystal structure, giving them a dark, uniform appearance.
They offer the highest efficiency among residential solar panels, typically ranging from 20% to 22%. While they come at a higher price point, they’re ideal for homes with limited roof space due to their superior performance.
Polycrystalline Panels
Polycrystalline panels consist of multiple silicon crystals, resulting in a speckled blue appearance. They’re generally less efficient than monocrystalline panels, with efficiency ratings around 15% to 17%.
However, they’re more affordable, making them a popular choice for homeowners with larger roof areas and budget constraints.
Thin-film Panels
Thin-film panels are lightweight and flexible, allowing for installation on curved or irregular surfaces. While they’re the least efficient option for residential use, typically around 10% to 13%, their unique construction makes them suitable for maximizing available surface area in certain situations.
2. Evaluating Solar Panel Efficiency
Understanding the types of solar panels is just the beginning. Next, it’s crucial to evaluate their efficiency, as this directly affects the amount of electricity your system can generate. Let’s examine what influences solar panel efficiency.
Conversion Efficiency
Conversion efficiency measures how effectively a panel converts sunlight into electricity. Higher efficiency panels require less surface area to produce the same amount of energy, making them particularly valuable when roof space is limited.
Factors Affecting Efficiency
Several factors impact panel efficiency, including temperature, shading, and orientation. Solar panels perform better at lower temperatures and when angled towards the sun. Partial shading from objects like tree branches can significantly reduce power output.
Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient indicates how temperature changes affect a panel’s efficiency. It’s expressed as a percentage per degree Celsius. A lower temperature coefficient means the panel’s performance is less susceptible to temperature increases, making it a desirable characteristic when comparing different panels.
3. Determining System Size
With a grasp of the types and efficiencies of solar panels, the next step is to determine the appropriate size of your solar panel system. This involves a few key calculations and considerations.
Calculating Energy Needs
To determine the right system size, start by calculating your daily energy usage. Review your electricity bills to find your average daily consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Alternatively, if you’re using solar for specific appliances, add up their individual energy requirements.
| Appliance | Rated (Running) Watts | Starting Watts |
| Air Conditioner | 2000 | 5000 |
| Ceiling Fan | 70 | 140 |
| Electric Oven | 5000 | 0 |
| Desktop Computer | 400 | 0 |
| Hair Dryer | 1800 | 0 |
| Water Heater | 4000 | 0 |
| Electric Kettle | 1500 | 0 |
| Humidifier | 50 | 0 |
| Dehumidifier | 600 | 800 |
| Electric Fireplace | 1500 | 0 |
| Window Fan | 75 | 150 |
| Electric Griddle | 1500 | 0 |
| Deep Freezer | 500 | 1000 |
| Printer | 50 | 0 |
| Electric Blanket | 200 | 0 |
| Rice Cooker | 700 | 0 |
| Treadmill | 2800 | 3500 |
| Sewing Machine | 100 | 0 |
| LED Light Bulb | 10 to 15 | 0 |
| Air Purifier | 60 | 0 |
Considering Roof Characteristics
Evaluate your roof’s size, shape, and orientation. South-facing roofs in the Northern Hemisphere typically receive the most sunlight. Also, consider any obstructions like chimneys or vents that might affect panel placement.
Estimating Number of Panels Required
Divide your daily energy needs by the average peak sun hours in your area and the rated power of your chosen panels. This calculation will give you a rough estimate of how many panels you’ll need to meet your energy goals.
4. Assessing Costs and Financing Options
Determining the right system size sets the stage for understanding the costs involved. Assessing the financial aspect of solar panels includes both the initial investment and potential long-term savings.
Upfront Costs
Solar panel systems involve significant upfront costs, typically ranging from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. The total cost depends on system size, panel quality, and installation complexity.
Long-term Savings and ROI
Calculate potential long-term savings by estimating reduced electricity bills over the system’s lifetime (usually 25-30 years). Consider factors like electricity rate increases and potential incentives to determine your return on investment (ROI).
Financing and Leasing Options
Explore various payment options:
- Cash purchase: Offers the highest long-term savings but requires a large upfront investment.
- Financing: Allows you to pay over time, but interest will reduce overall savings.
- Leasing: Provides immediate savings with little to no upfront cost, but offers lower long-term benefits and may not qualify for certain incentives.
5. Comparing Panel Quality and Durability
Cost and efficiency are important, but so is the quality and durability of the panels. High-quality panels ensure a long-lasting and reliable solar energy system.
Efficiency Ratings
Look for panels with high efficiency ratings, typically above 20% for premium options. Higher efficiency means more power generation in less space.
Warranties
Most high-quality panels come with 25-year performance warranties. Some manufacturers are now offering 30-year warranties, guaranteeing over 80% production after three decades.
Degradation Rates
Solar panels slowly lose efficiency over time. Look for panels with low degradation rates, ideally 0.25% per year or less. Some premium panels, like SunPower’s X-Series, guarantee 92% of minimum peak power after 25 years.
6. Installation Considerations
Choosing the right panels is only part of the equation. Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance and longevty of your solar panel system.
Roof Suitability
Ensure your roof is in good condition and can support the added weight of solar panels. If your roof needs replacing soon, it’s often best to do so before installing solar panels.
Orientation and Tilt
Optimal panel orientation is typically south-facing in the Northern Hemisphere. The ideal tilt angle depends on your latitude, but is generally between 30-40 degrees.
Professional vs. DIY Installation
While DIY installation can save money, professional installation ensures proper setup, adherence to local codes, and often comes with additional warranties. It’s usually recommended for most homeowners.
7. Selecting a Reputable Brand
With all technical and financial considerations covered, the final step is choosing a reputable brand. This ensures you get quality panels and reliable service.
Popular Manufacturers
REC and Q CELLS are among the most popular brands chosen by solar.com customers, known for their blend of performance and affordability. Other reputable brands include SunPower, Panasonic, and Silfab.
American-made Options
For those prioritizing American-made panels, options include Silfab (manufactured in Washington), Q CELLS (Georgia), and Mission Solar (Texas). Some U.S.-based companies like SunPower design panels domestically but manufacture overseas.
Bankability and Company Stability
Choose a manufacturer likely to be around to honor their 25-30 year warranty. Larger, established corporations like REC and Q CELLS are generally considered safe bets.
Conclusion
Selecting the best solar panel system for your home involves carefully considering various factors, from panel type and efficiency to system size and cost.
By understanding your energy needs, evaluating your roof characteristics, and comparing different panel options, you can make an informed decision that maximizes your long-term benefits.
Remember, the “best” solar panel system varies from home to home, so it’s crucial to work with a certified installer who can assess your specific situation and design a system tailored to your needs.
With the right solar panel system, you can significantly reduce your energy bills while contributing to a more sustainable future.