How Do You Calculate ROI For Solar Panels?

Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) for solar panels is crucial for homeowners considering this renewable energy option.
While the initial costs may seem daunting, understanding the potential financial benefits can help you make an informed decision.
ROI for solar panels measures how the cost of installation compares to the income generated or savings created over time.
On average, solar panel systems in the U.S. have an ROI of about 10%, meaning you’ll make an average profit of $10 for every $100 spent on your solar power system.
This article will guide you through the process of calculating solar panel ROI, factors that affect it, and help you determine if solar power is a worthwhile investment for your home.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel ROI
Before we delve into the calculation process, it’s important to understand the various factors that can impact your solar panel ROI:
Installation Costs
The upfront cost of installing solar panels is typically the most significant factor in determining ROI.
On average, a residential solar system can cost between $15,000 to $25,000, depending on the size and complexity of the installation. This includes the cost of equipment, labor, permits, and any necessary electrical upgrades.
It’s worth noting that installation costs have decreased significantly in recent years due to advancements in technology and increased competition in the solar industry.
Shopping around and getting multiple quotes can help you find the best deal for your solar panel installation.
Energy Bill Savings
One of the primary ways solar panels provide a return on investment is through reduced energy bills. By generating your own electricity, you’ll rely less on the grid and potentially eliminate your electric bill entirely.
The amount you save will depend on your energy consumption, local electricity rates, and the size of your solar system.
To estimate your potential savings, review your past electric bills and calculate your average monthly energy usage. Then, consult with a solar installer to determine how much of that usage your proposed solar system could offset.
Solar Incentives and Tax Credits
Government incentives and tax credits can significantly reduce the initial cost of your solar panel system, improving your ROI.
The most notable incentive is the federal solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which currently offers a 30% tax credit on the total cost of your solar system installation.
Many states and local municipalities also offer additional incentives, such as cash rebates, property tax exemptions, or performance-based incentives. Research the available incentives in your area to maximize your savings and improve your ROI.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
While solar panels generally require minimal maintenance, it’s important to factor in potential costs for cleaning, repairs, and component replacements over the system’s lifetime.
Most solar panels come with a 25-30 year warranty, but inverters may need replacement after 10-15 years. Set aside a small budget for annual maintenance and potential repairs to ensure your system continues to operate at peak efficiency.
Efficiency and Performance
The efficiency of your solar panels plays a crucial role in determining your ROI. Higher efficiency panels may cost more upfront but can generate more electricity over time, potentially leading to greater savings and a faster payback period.
Consider factors such as panel type (monocrystalline vs. polycrystalline), degradation rate, and warranty terms when selecting your solar panels.
Location and Sunlight Exposure
Your geographical location and the amount of sunlight your property receives directly impact your solar panel system’s performance and, consequently, your ROI.
Areas with more sunny days and higher electricity rates typically see better returns on solar investments. Factors such as roof orientation, shading from nearby trees or buildings, and local weather patterns should all be considered when estimating your potential solar energy production.
How to Calculate Solar Panel ROI
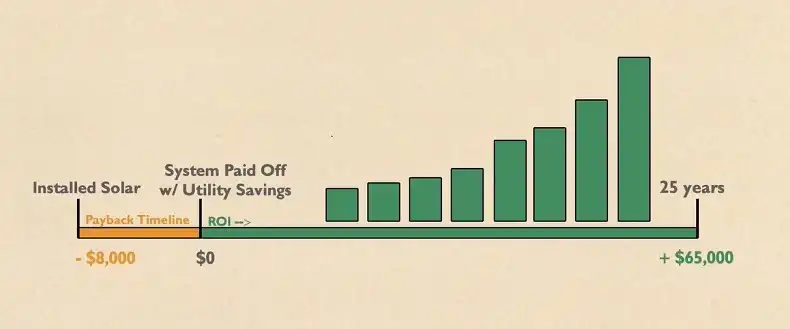
Now that we’ve covered the factors affecting ROI, let’s walk through the process of calculating it:
Basic ROI Formula The basic formula for calculating solar panel ROI is:
ROI = (Lifetime Savings – Initial Investment) / Initial Investment x 100%
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
- Determine your initial investment:
- Total cost of equipment and installation
- Subtract any applicable tax credits or incentives
- Estimate your annual energy savings:
- Calculate your current annual electricity costs
- Estimate the percentage of your electricity usage that will be offset by solar
- Project your lifetime savings:
- Multiply your annual savings by the expected lifespan of your solar system (typically 25-30 years)
- Factor in any potential increases in electricity rates over time
- Calculate your ROI:
- Subtract your initial investment from your lifetime savings
- Divide the result by your initial investment
- Multiply by 100 to get the percentage
Example Calculation
Let’s say you install a solar system with the following details:
- Initial cost: $20,000
- Federal tax credit: $6,000 (30% of $20,000)
- Net investment: $14,000
- Annual energy savings: $1,500
- System lifespan: 25 years
Lifetime savings:
$1,500 x 25 years = $37,500 ROI = ($37,500 – $14,000) / $14,000 x 100% = 167.86%
In this example, your solar panel system would provide a 167.86% return on investment over its lifetime.
Understanding the Solar Payback Period
While ROI gives you an overall picture of your investment’s profitability, the solar payback period helps you understand how long it will take to recoup your initial investment.
Definition of Solar Payback Period
The solar payback period is the time it takes for your energy savings to equal the cost of your solar panel system installation.
Payback Period Formula Payback Period = Initial Investment / Annual Energy Savings
Using our previous example: Payback Period = $14,000 / $1,500 = 9.33 years
This means it would take about 9 years and 4 months for your solar panel system to pay for itself through energy savings.
Factors Influencing Payback
Period Several factors can affect your solar payback period:
- Initial system cost
- Available incentives and rebates
- Local electricity rates
- System efficiency and energy production
- Changes in energy consumption
A shorter payback period generally indicates a better investment, but it’s important to consider the long-term savings potential beyond the payback period as well.
Additional Considerations
When evaluating the ROI of solar panels, there are a few additional factors to keep in mind:
Net Metering
Programs Many utility companies offer net metering programs, which allow you to sell excess electricity back to the grid. This can further improve your ROI by providing credits on your electric bill or even generating additional income.
Property Value
Increase Installing solar panels can increase your home’s value. Studies have shown that homes with solar panels sell for a premium compared to similar homes without solar. This added value should be factored into your overall ROI calculation.
Long-Term Savings
Potential Remember that your solar panel system will continue to generate savings long after it has paid for itself. Consider the potential for increased electricity rates over time, which could make your solar investment even more valuable in the future.
How Solar Panels Pay for Themselves
It’s important to understand how solar panels actually pay for themselves over time:
Reduced Energy Bills
The primary way solar panels provide a return on investment is through reduced energy bills. By generating your own electricity, you’ll rely less on the grid and potentially eliminate your electric bill entirely.
Most households can expect to save an average of $1,500 per year or $125 per month on utility bills after installing a typical 6-kilowatt solar power system.
Solar Incentives and Tax Credits
Government incentives and tax credits can significantly reduce the initial cost of your solar panel system, improving your ROI.
The most notable incentive is the federal solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which currently offers a 30% tax credit on the total cost of your solar system installation.
Many states and local municipalities also offer additional incentives, such as cash rebates, property tax exemptions, or performance-based incentives.
Increased Property Value
Installing solar panels can increase your home’s value. Studies have shown that homes with solar panels sell for a premium compared to similar homes without solar. This added value should be factored into your overall ROI calculation.
Conclusion
Calculating the ROI for solar panels is an essential step in determining whether this renewable energy option is right for your home. While the initial investment may seem significant, the long-term financial benefits can be substantial.
With an average ROI of around 10% and payback periods typically ranging from 8 to 13 years, solar panels can be a smart financial decision for many homeowners.
When considering solar panel installation, be sure to factor in installation costs, energy savings, available incentives, maintenance expenses, and your local climate.
By carefully evaluating these factors and using the calculation methods outlined in this article, you can make an informed decision about whether solar panels are a worthwhile investment for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Is The Typical ROI On Solar Panels?
The typical Return on Investment (ROI) on solar panels is around 10%. This means that for every $1,000 invested in a solar panel system, you can expect to receive $100 in savings or income annually, making it a financially sound investment over the long term.
2. How Do You Calculate Payback On Solar Panels?
To calculate the payback on solar panels, divide the net cost of the system (total cost minus any incentives or rebates) by the annual savings on your electricity bill. This will give you the number of years it takes for the system to pay for itself through energy savings.
3. What Is A Good Payback For Solar Panels?
A good payback period for solar panels is typically between six to 10 years. This timeframe indicates that the investment in solar panels will be recouped within a decade, after which the energy savings continue to provide financial benefits.
4. How Do You Calculate Solar Panel Revenue?
You calculate solar panel revenue by multiplying the total power generation of your solar system (in kilowatt-hours) by the average daily sun hours and the price of electricity. Subtracting your daily costs from this amount gives you the net revenue generated by your solar panels.
5. Do Solar Panels Actually Save You Money?
Yes, solar panels actually save you money by reducing or even eliminating your electricity bills. By generating your own power, you decrease your reliance on the grid, which leads to significant long-term savings. Additionally, excess energy can often be sold back to the grid, providing further financial benefits.






