What Components Are Necessary for an Off-Grid Solar System

Off-grid solar systems are standalone electricity generation systems that operate independently of the traditional power grid. These systems harness the power of the sun to provide a reliable and sustainable source of energy for homes, cabins, RVs, and even emergency backup power. By going off-grid, homeowners and remote dwellers can enjoy the benefits of energy independence, reduced environmental impact, and long-term cost savings.
However, designing and installing an off-grid solar system requires careful consideration of various components and their compatibility to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Core Components for Off-Grid Solar System
- Solar Panels
At the heart of any off-grid solar system are the solar panels, which convert sunlight into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. The three main types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Monocrystalline panels are typically the most efficient, with conversion rates ranging from 15% to 22%, while polycrystalline panels are slightly less efficient at 13% to 16%. Thin-film panels, on the other hand, have a lower efficiency of around 10% to 12% but can be more cost-effective and flexible in their installation.

When selecting solar panels for an off-grid system, it’s essential to consider factors such as wattage, voltage, temperature coefficient, and the manufacturer’s reputation. Panels with higher wattage and efficiency will generate more power, but they may also come at a higher cost. Additionally, understanding the temperature coefficient is crucial, as it indicates how the panel’s performance will be affected by temperature fluctuations.
- Solar Charge Controllers
The solar charge controller is a critical component that regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the battery bank, preventing overcharging and ensuring the batteries’ longevity. There are two main types of charge controllers: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT).
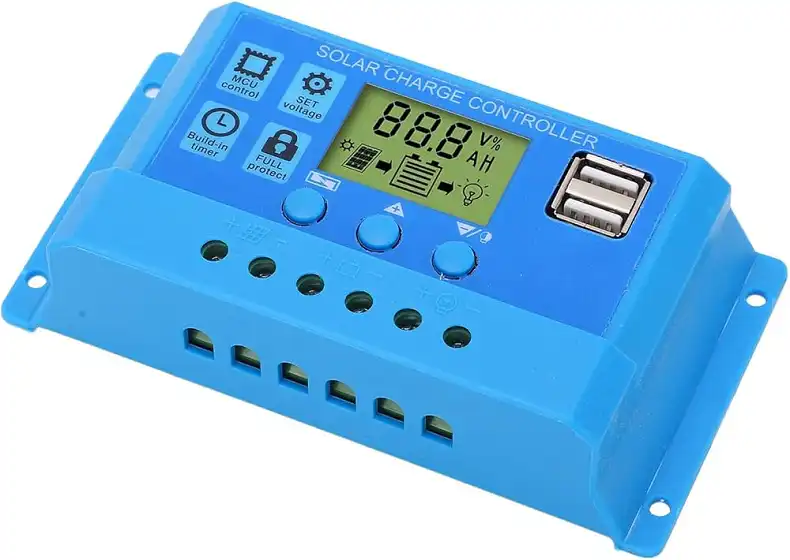

PWM charge controllers are the more traditional and less expensive option, but they are less efficient at converting the solar panel’s output to the optimal voltage for charging the batteries. MPPT charge controllers, on the other hand, are more sophisticated and can extract the maximum power from the solar panels, resulting in a more efficient charging process. The choice between PWM and MPPT charge controllers will depend on the specific requirements of your off-grid solar system, such as the size of the solar array and the battery bank.
- Batteries
Batteries play a crucial role in off-grid solar systems, serving as the energy storage solution to power your home or appliances during periods of low sunlight or nighttime. The most common battery technologies used in off-grid systems include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-cadmium.
Lead-acid batteries are the most affordable option, but they have a shorter lifespan and require more maintenance. Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are more expensive but offer a longer cycle life, higher energy density, and lower maintenance requirements. Nickel-cadmium batteries fall somewhere in the middle, with moderate cost and performance characteristics.

When selecting batteries for your off-grid system, consider factors such as capacity (measured in amp-hours or watt-hours), voltage, discharge rate, and compatibility with the other components in your system. It’s also essential to design the battery bank properly, ensuring the right number of batteries are connected in series and parallel to meet your energy needs.
| Battery Type | Cost | Lifespan | Depth of Discharge | Maintenance |
| Lead-Acid | Low | 3-5 years | 50% | High |
| Lithium-Ion | High | 7-10 years | 80% | Low |
| Nickel-Cadmium | Medium | 5-7 years | 70% | Medium |
Table: Comparison of Common Battery Technologies for Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Inverters
The inverter is the component responsible for converting the Direct Current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into Alternating Current (AC) electricity, which is the standard format used by most household appliances and electrical devices.
There are two main types of inverters used in off-grid solar systems: pure sine wave and modified sine wave. Pure sine wave inverters produce a clean, sinusoidal waveform that is identical to the electricity provided by the grid, making them compatible with a wide range of electronics and appliances. Modified sine wave inverters, on the other hand, produce a less-refined waveform, which may not be suitable for some sensitive electronic devices.
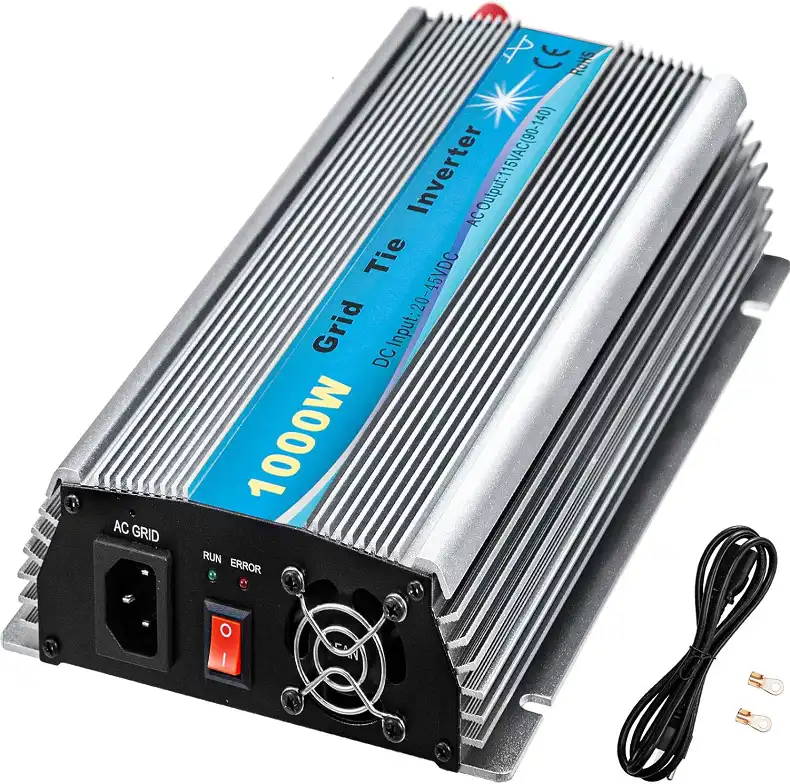

When selecting an inverter, consider factors such as the continuous and surge power output, efficiency, and safety features like overload and short-circuit protection. Choosing an inverter with the right capacity to meet your energy needs is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of your off-grid solar system.
Additional Components for Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Mounting Systems
Solar panels need to be securely mounted to withstand environmental factors like wind and snow loads. There are two primary types of mounting systems: roof-mounted and ground-mounted.
Roof-mounted systems are a popular choice for homes and buildings, as they utilize existing roof space and can be integrated seamlessly into the structure. Ground-mounted systems, on the other hand, are more suitable for remote or open-space installations, but they require additional land and may be more susceptible to shading from nearby obstacles.
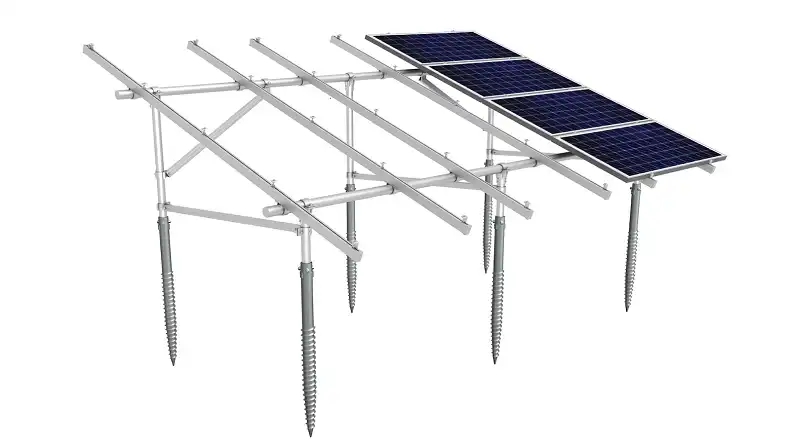

When selecting a mounting system, consider factors such as the roof type, tilt angle, and wind load requirements to ensure the solar panels are installed safely and securely.
- Wiring and Connectors
Proper wiring and high-quality connectors are essential for the safe and efficient operation of an off-grid solar system. It’s important to use the appropriate wire types, such as MC (Metal Clad) cable or specialized DC and AC wiring, which are designed to withstand outdoor conditions and potential electrical hazards.
Careful attention must be paid to wire sizing to prevent overloading and potential fire hazards. Additionally, the use of circuit breakers and fuses is crucial for protecting the system and its components from electrical overloads or short circuits.
- Backup Generators (Optional)
While off-grid solar systems are designed to provide a reliable source of electricity, there may be instances where extended periods of cloudy weather or high energy demands can deplete the battery bank. In such cases, a backup generator can serve as a supplementary power source, ensuring that your off-grid system maintains its functionality.
Backup generators can be powered by various fuels, such as gasoline, propane, or diesel, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, efficiency, and environmental impact. When integrating a backup generator with your off-grid solar system, it’s essential to ensure seamless integration and compatibility between the two systems.
System Design and Sizing
Designing an off-grid solar system requires a careful analysis of your energy consumption needs, geographic location, and budget constraints. Accurate load calculations are the foundation of the system design, as they determine the required capacity of the solar panels, batteries, and inverters.
To begin, estimate your daily or monthly energy consumption based on the appliances and devices you plan to power. This information, combined with your location’s average sun hours, will help you calculate the necessary solar panel size and battery storage capacity to meet your energy demands.
Online tools and resources are available to assist with system design and sizing, providing guidance on component selection and system configuration to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Installation and Maintenance
Off-grid solar systems can be installed either by a professional solar installer or through a DIY approach, depending on your technical expertise and comfort level. Professional installation ensures proper wiring, component integration, and adherence to safety regulations, but it may come at a higher cost. DIY installation, on the other hand, offers the opportunity to save money, but it requires a deeper understanding of electrical systems and safety protocols.
Regardless of the installation method, maintaining your off-grid solar system is crucial for its long-term performance and reliability. This includes regular cleaning of the solar panels, checking electrical connections, and properly maintaining the battery bank. Addressing any issues promptly, such as low battery voltage or inverter faults, can help prevent more serious problems down the line.
Final Words
Off-grid solar systems offer a self-sufficient and sustainable power solution for those living in remote areas or seeking to reduce their reliance on the traditional power grid. By understanding the key components of an off-grid solar system, including solar panels, charge controllers, batteries, and inverters, you can design and install a system that meets your specific energy needs.
As off-grid solar technology continues to evolve, with advancements in battery storage and microinverter technology, the feasibility and accessibility of these systems are steadily improving. By making the switch to off-grid solar, you not only gain energy independence but also contribute to a cleaner, more environmentally friendly future.


![[Explored] Can You Use Mirrors To Redirect Sunlight On Solar Panels?](https://www.itekenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/can-you-use-mirrors-to-redirect-sunlight-768x428.webp)


![[Answered] Do I Need to Turn Off Solar Panels to Clean?](https://www.itekenergy.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Do-I-Need-to-Turn-Off-Solar-Panels-to-Clean-768x428.webp)
