Setting Up And Maintaining A Solar Panel Battery Bank
Setting up and maintaining a solar panel battery bank is a crucial step in maximizing the benefits of your solar energy system.
A well-designed battery bank allows you to store excess solar power for use during nighttime or cloudy days, increasing your energy independence and potentially reducing your electricity bills.
The key to a successful solar battery setup lies in proper sizing, installation, and ongoing maintenance.
By following best practices for battery care and management, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your batteries and optimize their performance.
This guide will walk you through the essential aspects of creating and maintaining an efficient solar battery bank, helping you make the most of your renewable energy investment.
Understanding Solar Battery Banks

Solar battery banks are an integral part of many solar power systems1, working in tandem with solar panels to provide a reliable and sustainable energy solution.
Before diving into the specifics of setup and maintenance, it’s important to understand what a solar battery bank is and how it functions within your solar energy system.
What Is A Solar Battery Bank?
A solar battery bank is essentially a collection of batteries designed to store excess electricity generated by your solar panels during peak sunlight hours.
This stored energy can then be used during periods of low or no sunlight, such as cloudy days or at night.
Think of it as your personal energy reservoir, allowing you to maintain a consistent power supply even when your solar panels aren’t actively producing electricity.
Components Of A Solar Battery System
A typical solar battery system consists of several key components:
- Solar Panels: These capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Charge Controller: This device regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging and extending battery life.
- Battery Bank: A group of batteries that store the electricity generated by the solar panels.
- Inverter: This converts the stored DC (direct current) electricity in the batteries to AC (alternating current) electricity, which is what most household appliances use.
How Solar Battery Banks Work
The process begins with your solar panels capturing sunlight and converting it into DC electricity. This electricity then flows through the charge controller, which ensures it’s delivered to the battery bank at the correct voltage.
Once the electricity reaches the battery bank, it’s stored for future use. When you need to use the stored energy, the electricity flows from the battery bank to the inverter.
The inverter converts the DC electricity to AC electricity, making it usable for your household appliances. This entire process ensures that you have a steady and reliable power supply, even during nighttime or cloudy days.
Sizing and Designing Your Solar Battery Bank
Properly sizing and designing your solar battery bank is crucial for ensuring that it meets your energy needs efficiently and cost-effectively.
This process involves several key considerations, from determining the right capacity to choosing the most suitable battery type and configuration.
Determining Battery Bank Capacity
The capacity of your battery bank should be sized to meet your energy needs during periods when your solar panels aren’t producing electricity. Here are some factors to consider:
- Daily energy consumption: Calculate your average daily energy usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Days of autonomy: Decide how many days you want to be able to run solely on battery power without solar input. This is typically 3-5 days for most residential systems.
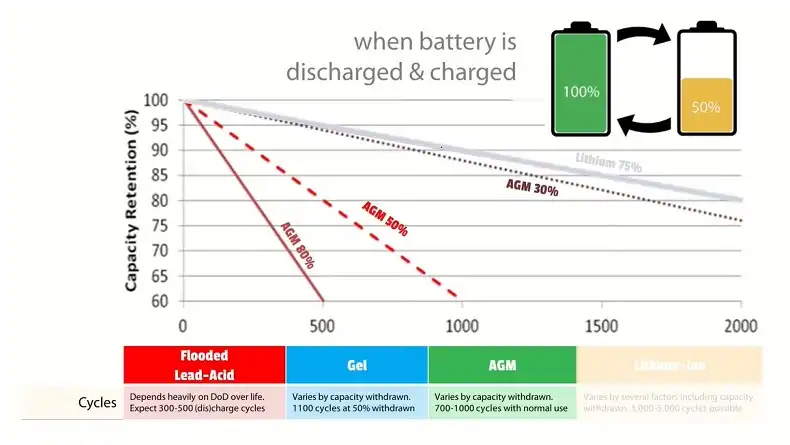
- Depth of discharge: Most batteries shouldn’t be discharged below a certain level to maintain their longevity. For example, lead-acid batteries typically shouldn’t be discharged below 50% capacity.
As a general rule, your battery bank should be sized to a capacity of at least 5 days of load. However, it’s often advisable to size larger than this, as energy use in most home power systems tends to increase over time.
Choosing the right battery type
There are several types of batteries available for solar energy storage, each with its own advantages and considerations:
- Lead-acid batteries: These are the most common and affordable option. They come in two main types:
- Flooded lead-acid: Require regular maintenance but are the least expensive.
- Sealed lead-acid (AGM and Gel): Maintenance-free but more expensive.
- Lithium-ion batteries: More expensive upfront but offer longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and deeper discharge capabilities.
- Flow batteries: Offer very long cycle life and the ability to fully discharge without damage, but are typically more expensive and complex.
When choosing a battery type, consider factors such as initial cost, lifespan, maintenance requirements, and performance characteristics.
Configuring Batteries (Series Vs Parallel)
The way you connect your batteries can affect the overall voltage and capacity of your battery bank:
- Series connection: Batteries are connected end-to-end (positive to negative). This increases the voltage while keeping the capacity (amp-hours) the same.
- Parallel connection: Batteries are connected positive-to-positive and negative-to-negative. This increases the capacity while keeping the voltage the same.
- Series-parallel connection: A combination of both methods to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
It’s generally advisable to avoid multiple parallel strings of batteries, as this can lead to imbalances and reduced overall performance. Ideally, aim for a single series of cells sized appropriately for your needs.
By carefully considering these factors and working with a qualified solar installer, you can design a solar battery bank that provides reliable, efficient energy storage for your home or business.
Installation and Setup Of A Solar Panel Battery Bank
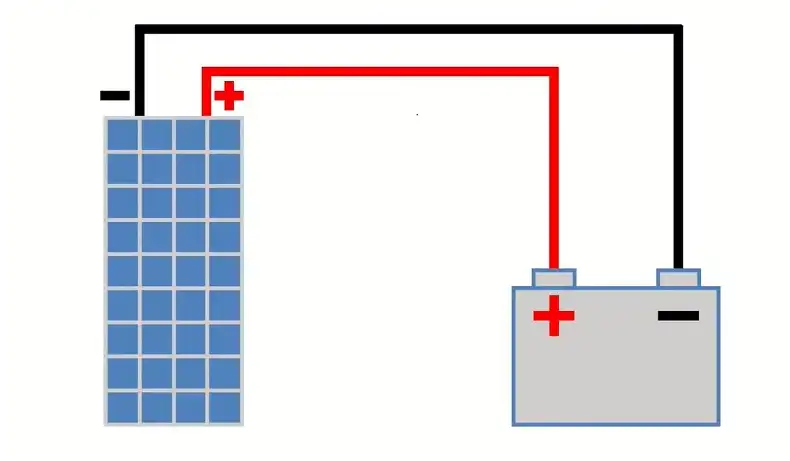
Proper installation and setup of your solar battery bank are crucial for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and safety.
This process involves careful consideration of placement, wiring, and integration with other components of your solar power system.
Proper Placement And Environmental Considerations
The location of your battery bank can significantly impact its performance and lifespan:
- Temperature control: Batteries perform best in moderate temperatures. Extreme heat or cold can reduce efficiency and shorten battery life. If possible, install batteries in a temperature-controlled space.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation, especially for flooded lead-acid batteries which can release gases during charging.
- Accessibility: Place batteries in an area that’s easily accessible for maintenance and inspection.
- Protection: Shield batteries from direct sunlight and moisture.
- Floor considerations: For flooded batteries, consider installing them over a floor drain or in a space without a floor for easy rinsing and cleaning.
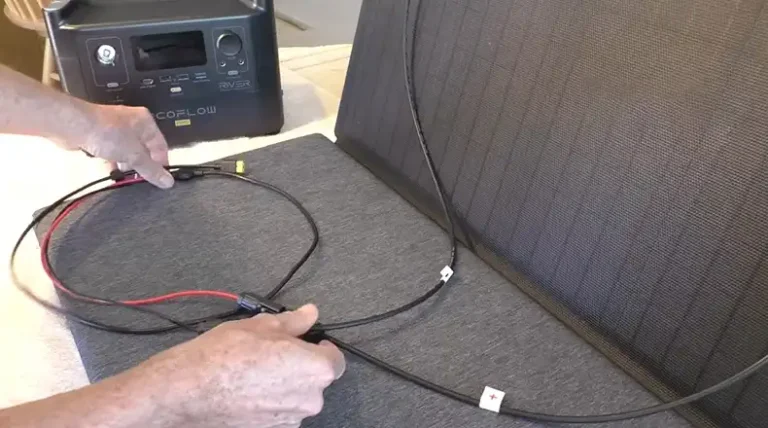
Wiring and connections
Proper wiring is essential for safety and efficiency:
- Use appropriate gauge wires: Ensure wires are thick enough to handle the current flow without overheating.
- Make secure connections: Loose connections can cause resistance, leading to heat build-up and potential fire hazards.
- Protect against corrosion: Apply a non-hardening sealant to all metal parts of the terminals before assembly. This prevents corrosion, which can cause resistance and potential hazards.
- Maintain symmetry: When wiring multiple battery strings, connect the two main cables to opposite corners of the battery bank and maintain symmetry in wire size and lengths. This helps distribute current evenly through the bank.
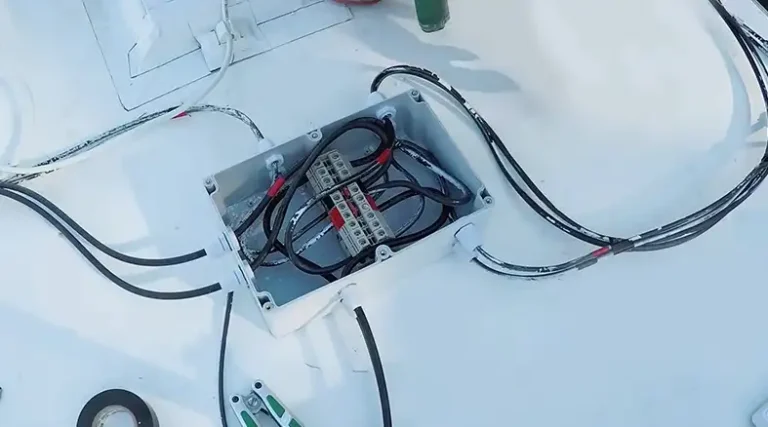
Integration With Solar Panels And Charge Controllers
Proper integration of your battery bank with other system components is key to efficient operation:
- Charge controller selection: Choose a charge controller that’s compatible with your battery type and sized appropriately for your solar array.
- Temperature compensation: Use temperature compensation features in your charge controller to adjust charging parameters based on battery temperature.
- Inverter integration: Ensure your inverter is compatible with your battery bank’s voltage and can handle the required power output.
- System monitoring: Install a battery monitoring system to keep track of your battery bank’s state of charge, voltage, and overall health.
Remember, while some DIY enthusiasts may feel comfortable installing their own solar battery systems, it’s often best to work with a qualified solar installer.
They can ensure that all components are properly sized, installed, and integrated for optimal performance and safety.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance and care are essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your solar battery bank. Regular attention to your batteries can prevent many common issues and ensure optimal performance over time.
Regular Inspections And Cleaning
- Visual inspections: Conduct monthly visual inspections of your battery bank. Look for signs of corrosion, leakage, or physical damage.
- Cleaning: For flooded lead-acid batteries, clean the battery tops about twice per year. This removes accumulated moisture (acid spatter) and dust, which can reduce corrosion and prevent stray currents from stealing energy.
- Check connections: Regularly inspect and tighten all connections to ensure they remain secure and free from corrosion.
- Water levels: For flooded lead-acid batteries, check water levels monthly and top up with distilled water as needed. Never add anything other than distilled water, deionized water, or very clean rainwater collected in plastic containers.
Monitoring Battery Health And Performance
- State of charge: Regularly monitor the state of charge of your batteries. For flooded lead-acid batteries, use a hydrometer to measure the specific gravity of the electrolyte in each cell.
- Voltage checks: Monitor battery voltage regularly. Abnormal voltage readings can indicate issues with individual batteries or the charging system.
- Capacity testing: Periodically conduct capacity tests to ensure your batteries are maintaining their rated capacity.
- Use monitoring systems: Consider installing a battery monitoring system that can provide real-time data on battery performance, including state of charge, voltage, and current flow.
Addressing Common Issues
- Corrosion: If you notice corrosion on battery terminals, clean it off immediately using a mixture of baking soda and water. Rinse with clean water and dry thoroughly before reapplying terminal protection.
- Temperature effects: Monitor battery temperature and take steps to moderate it if necessary. Batteries lose capacity in cold temperatures and can deteriorate faster in high temperatures.
- Equalization: For flooded lead-acid batteries, perform periodic equalization charges to balance the cells and prevent stratification of the electrolyte.
- Uneven charging: If you notice some batteries in a bank are consistently undercharged, it may indicate a problem with cell balance or connections. Have this checked by a professional.
Remember, different battery types have different maintenance requirements. Lithium-ion batteries, for instance, generally require less maintenance than lead-acid batteries. Always refer to your battery manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance instructions.
Maximizing Battery Life and Efficiency
To get the most out of your solar battery bank, it’s crucial to implement practices that maximize battery life and efficiency. By following these guidelines, you can extend the lifespan of your batteries and ensure they operate at peak performance.
Proper Charging And Discharging Practices
- Avoid deep discharges: While deep-cycle batteries are designed to handle deeper discharges than standard batteries, it’s still best to avoid completely draining them. For lead-acid batteries, try not to discharge below 50% of their capacity. Lithium-ion batteries can typically handle deeper discharges.
- Regular full charges: Bring your batteries to a full state of charge at least every 3 weeks. This reduces internal corrosion and degradation, and helps ensure equalization so that weaker cells don’t fall continually farther behind.
- Use appropriate charge rates: Charge your batteries at the rate recommended by the manufacturer. Charging too quickly can damage the batteries, while charging too slowly can lead to sulfation in lead-acid batteries.
- Implement low-voltage disconnects: Use low voltage disconnect (LVD) devices in your load circuits to prevent over-discharge, which can cause immediate, irreversible loss of capacity and life expectancy.
Temperature Management
- Maintain consistent temperature: Try to keep your batteries at a consistent, moderate temperature. Extreme heat or cold can significantly impact battery performance and lifespan.
- Use temperature compensation: If your charge controller has a temperature compensation feature, use it. This adjusts charging parameters based on battery temperature, preventing overcharging in hot conditions and undercharging in cold conditions.
- Insulation: In colder climates, consider insulating your battery enclosure to maintain a more stable temperature.
Using Battery Monitoring Systems
- Install a system monitor: A good monitoring system can provide valuable data on your battery bank’s performance, including state of charge, voltage, and current flow.
- Regular data review: Regularly review the data from your monitoring system to identify any trends or issues that may need addressing.
- Set alerts: Configure your monitoring system to alert you to potential issues, such as low voltage or high temperature conditions.
- Use the data for optimization: Use the information from your monitoring system to optimize your energy usage patterns and charging cycles.
Conclusion
Setting up and maintaining a solar panel battery bank is a significant undertaking, but one that can greatly enhance the value and efficiency of your solar power system.
By properly sizing your battery bank, choosing the right type of batteries, and following best practices for installation and maintenance, you can create a reliable and long-lasting energy storage solution.
Remember, the key to a successful solar battery system lies in careful planning, regular maintenance, and optimal usage practices.