Solar PV Panels Mono vs Poly | How Do I Compare Them
Although there are so many solar PV panels available in the market today, the two main types are mono and polycrystalline panels. And when it comes to choosing the one between the two, the main consideration comes down to efficiency and budgetary concerns.
Among the two, monocrystalline panels tend to be more efficient in converting sunlight into electricity. However, this doesn’t come without its caveats. They tend to be usually costlier. Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are less efficient and take up a bit more space, however, they are way cheaper.
Below, I have discussed in detail, how the two types of panels compare against each other and how you can decide what type of panel is the ideal one for you.
What are Monocrystalline Solar PV Panels
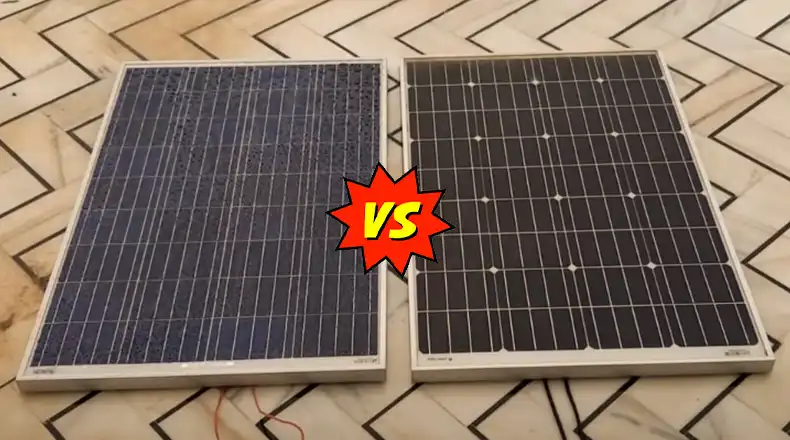
Monocrystalline solar panels go by the shorthand name “mono panels.” They are constructed from photovoltaic silicon cells made by melting a single crystalline silicon ingot and slicing the uniform wafer-thin layers into cell units. Aligning and connecting these cells creates the typical mono panel with its distinctive black color and visible silicon cell structure for efficiently absorbing sunlight.
What are Polycrystalline Solar PV Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels use what’s known as multicrystalline silicon cells and get the shorthand name of “poly panels.” They are manufactured from molten fragments of varied silicon crystallites that are melted and set together in a cake mold, then similarly cut and processed into cell units ready for panel assembly. This polycrystalline formation process results in solar cells with a somewhat randomized crystalline structure, visible in the speckled bluish hue of the common poly panel.
How Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline Panels Work
Both mono and poly solar panels use rows of photovoltaic silicon cells wired together to convert absorbed solar photon energy into usable DC electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Essentially, sunlight transfers its energy to excite the panel’s silicon electrons enough to set them loose, creating current flow. That flow gets redirected as electric power is ready for stable output, battery storage, or grid transmission.
Mono Vs Poly Solar PV Panels
We’ll start things off with a simple comparison table between the mono and poly solar PV panels.
| Monocrystalline (Mono) Panels | Polycrystalline (Poly) Panels |
| Higher efficiency – averages 15-18% | Lower efficiency – averages 13-16% |
| More expensive per watt | Less expensive per watt |
| Require less roof space | Require more roof space |
| All black color uniformity | Blue speckled color |
| Longer lifespans (25-30 years) | Shorter lifespans (20-25 years) |
| Lower heat tolerance | Higher heat tolerance |
| Better low-light performance | Worse low-light performance |
| Higher iron content | Lower iron content |
Now let’s break down the table.
Efficiency levels
On average, monocrystalline solar panels have module efficiency in the 15-18% range. This means they can convert 15-18% of the sunlight energy they absorb into usable electricity through their orderly aligned silicon crystal cell structure. By contrast, the random crystal formation of poly panels leads to slightly lower efficiency capabilities averaging 13-16% sunlight conversion.
Cost factors
The complex process used to grow uniform monocrystalline silicon boules suitable for cell-slicing comes at a premium price. Monocrystalline solar has a reputation for better efficiency but also moderately higher per-kilowatt-hour costs. However, mono panels offset this pricing gap over the long term through energy production nearing the maximum potential from available sunlight.
Rooftop real estate constraints
With their edge in conversion efficiency, monocrystalline panels can squeeze more watts per square meter out of limited roof space or awkward angles that lack room for large arrays. For property owners lacking wide-open southern exposure, mono is typically the way to maximize solar generation.
Aesthetic appeal and longevity
For curb appeal reasons some homeowners prefer the look and even shading effects of uniform black monocrystalline panels over the mottled sky blue patterning of traditional poly panels. Moreover, the tightly aligned silicon crystal structure of quality mono panels enhances their working lifespans. Properly maintained, they often perform for 30 years or longer before significant cell efficiency degradation.
Temperature resistance advantages
When ambient heat levels rise drastically, poly panels tend to sustain their electrical output a bit better. Hot summer days can knock a few percentage points off mono panel peak performance temporarily. This heat tolerance makes polycrystalline silicon tech a potentially smart bet for homes in extremely hot desert climates.
Installation and Mounting
Both monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels are lightweight enough these days to mount securely on most standard rooftops without requiring major structural reinforcements. Poly panels tend to be slightly thicker than mono options, but the difference in weight per square foot is negligible – around 1 to 3 pounds typically. Installation process and racking needs are nearly identical between the two photovoltaic technologies. Homeowners can expect a smooth trouble-free solar setup without worrying about panel variety choice stressing the roof itself during or after the fact.
How to Pick the Right Solar PV Panel Type for You
When deciding between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, there are several factors to take into account:
Assess Your Roof Size and Layout
If you have limited roof space, monocrystalline is likely the better choice, as these panels can produce more watts per square foot due to higher efficiency rates.
If you have plenty of wide, south-facing exposure, polycrystalline can maximize square footage more cost-effectively.
Evaluate Local Climate Conditions
In extremely hot climates where temperatures exceed 100°F routinely, heat-tolerant polycrystalline panels may maintain energy output better long-term.
In more temperate or partially-shaded locations, monocrystalline panels can leverage peak efficiency ratings when conditions permit.
Compare Pricing Based on Required System Size
Due to higher per-watt costs for mono, smaller systems under 5 kW or so may favor more affordable poly, while larger installs can better leverage superior mono economics through sheer scale.
Local electric rates also determine payback period. High prices per kWh may justify springing for premium monocrystalline despite steeper initial panel expense.
Assess Your Budget Horizon
For homeowners planning to stay long-term or seeking robust energy production decades down the road, higher-quality mono panels with 35+ year lifespans are worth considering.
Prioritize Aesthetics
If panel appearance from street view matters, some homeowners prefer the consistent jet-black hue of orderly monocrystalline arrays.
Maintenance Considerations
Very little routine maintenance is required once monocrystalline or polycrystalline systems are up and running. Rain and wind keep panels reasonably clean in most regions, but a quick spray down with a garden hose can clear off any accumulated dust if desired once or twice per year. Check electrical conduits annually to ensure secure connections and no critter interference. Also inspect roof attachment points to be sure panels remain properly anchored, adjusting if needed. Beyond that, sit back and soak up free daylight energy! Manufacturers predict only around 0.5% efficiency loss per twelve-month period.
FAQ
Are there solar rebates for going mono vs poly?
Federal and state solar incentives generally do not differentiate between panel types. Some local utility rewards for efficiency may indirectly favor monocrystalline installs producing more energy yearly. Always confirm regional rebates before deciding.
Can you combine mono and poly solar panel types?
It is technically possible but generally not advisable for aesthetic reasons and system complexity. Mono and poly panels have differing electrical outputs requiring specialized system configuration for pairing. Keeping solar arrays uniform in appearance and electrical properties is usually recommended.
What are bifacial solar panels?
Bifacial panels absorb light on both sides, potentially boosting energy collection 10-15% annually in the right installations. They cost more but the dual-side functionality helps leverage production over time. Bifacial tech is available in both monocrystalline and polycrystalline panel types.