What Factors Can Affect the Production of Electricity in a Solar Power Plant?
Solar power has emerged as a leading renewable energy source worldwide. Massive solar farms with thousands of photovoltaic panels are being built across the globe to provide clean electricity. But many complex factors can affect how much electricity a solar plant ultimately produces. Understanding these key variables is essential for optimizing the design and performance of solar installations.

External Environmental Factors
Solar Irradiance and Insolation
The amount of sunlight reaching the solar arrays is the most fundamental factor determining energy output. Called solar irradiance, this is measured in watts per square meter. Areas with consistently high irradiance have greater solar power potential. Insolation accounts for irradiance over time and is measured in kilowatt-hours per square meter. Factors like location, time of day, weather, and seasons all impact irradiance and insolation levels.
Temperature and Weather
Ambient temperature affects solar panel efficiency. As temperature increases, panel efficiency decreases. Hot sunny days may seem ideal but often result in lower energy production. Cloud cover, pollution, rain, and snow also reduce sunlight exposure. Solar plants in cold, dry climates can leverage snow’s reflected light.
Shading
Objects like buildings, trees, or terrain that cast shadows on solar arrays greatly reduce electricity generation from shaded panels. Careful site selection and panel layouts optimized for minimal shading are essential. Nearby vegetation may require trimming to reduce shading.
Soiling
Dust, dirt, bird droppings, sand, and other grime accumulating on panels, called soiling, can block sunlight and reduce energy absorption. Regular panel cleaning is key to maximizing solar plant production. Soiling issues are greater in agricultural and desert areas.
Wind and Wildlife
Strong winds can damage solar tracking equipment and dislodge panels. Birds and insects attracted to solar plants contribute to soiling. Proper engineering helps withstand high winds. Wildlife deterrents like reflective tape combat soiling.
Solar Panel Factors
Photovoltaic Cell Technology and Efficiency
Converting sunlight into electricity comes down to photovoltaic cell technology. Different semiconductor materials, like monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, and thin-film, have varying solar conversion efficiencies. Selecting the most efficient yet cost-effective panels maximizes energy yield.
Panel Orientation and Tilt
Panels angled to optimize sun exposure for a site’s latitude and climate produce more energy. Tracking systems rotating panels to follow the sun’s daily and seasonal movement also boost productivity.
Panel Degradation
Solar panels gradually lose efficiency over decades of use. Weathering, thermal stresses, and material degradation all contribute. Proper solar panel maintenance and periodic replacement help counteract degradation.
Panel Soiling and Connectivity
Soiling and dust on panels reduces their productivity over time. Loose wiring and electrical faults in panels and arrays also cut energy output unless corrected.
Balance of System Factors
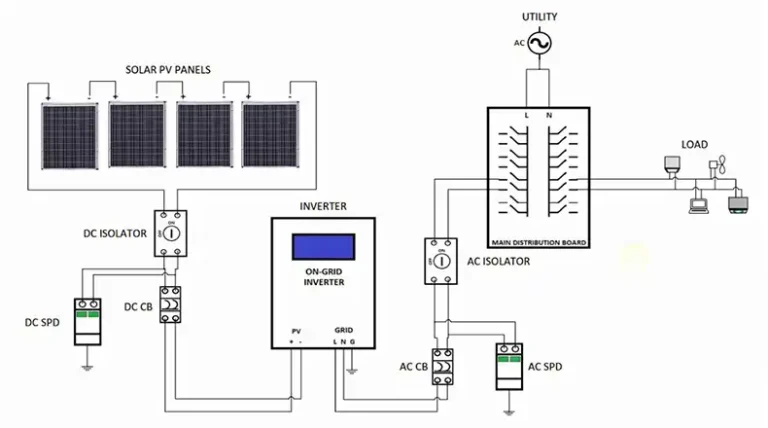
Inverters and Transformers
Inverters convert the DC electricity from solar panels into AC for grid integration. Inverter outages bring production to a halt. Transformers step-up voltages for transmission over long distances.
Monitoring and Control Systems
Extensive monitoring and automated control systems track solar plant performance and identify issues for quick response. This helps minimize downtime and output losses.
Energy Storage
Onsite batteries store excess solar energy for later use. This allows higher use of peak capacity and smooths production variability.
Grid Integration
Connecting solar plants to the utility grid poses complex challenges. Grid stability issues and inadequate solar integration can force solar plants to curtail production.
Cables and Wiring
Electrical losses occur as current travels through cables and wires. Proper system design ensures minimal resistive losses.
How to Increase the Production of Solar Electricity
Cleaning and Inspection
Regular solar panel washing, maintenance checks, and equipment inspections help achieve optimal performance and lifespan. Staff training is key.
Testing and Repairs
Spotting and quickly fixing any failed components like inverters or tracking motors is crucial for maximizing uptime.
Vegetation Management
Trimming back nearby plant growth blocking sunlight or damaging equipment avoids shading and soiling issues.
Monitoring and Analysis
Continuously monitoring energy output metrics and weather data informs optimization efforts. Unexpected variations are promptly investigated.
Final Words
A wide range of factors related to equipment, weather, operations, and maintenance affect solar power plant productivity. Careful system design, site selection, component choice, and ongoing maintenance best mitigate these variables. As solar technology improves, future plants will likely achieve greater power output and overcome current limitations.
Solar Power Production FAQs
How does weather impact solar power output?
Weather conditions like clouds, rain, snow, and air pollution can reduce the amount of sunlight reaching solar panels, lowering electricity generation. Hot temperatures also decrease panel efficiency. Solar plants work best in sunny, temperate climates.
Why does solar energy vary throughout the day?
Solar power output follows the sun’s daily movement, peaking when irradiance is strongest midday and falling off in the morning and late afternoon. Solar tracking systems can mitigate this.
How does panel tilt and orientation affect production?
Panels angled to optimize sun exposure for a site’s latitude and climate will produce more energy annually. Facing south in the northern hemisphere or north in the southern hemisphere is optimal in most regions.
How often should solar panels be cleaned?
Frequency depends on soiling levels, but panels should be cleaned every few weeks at minimum. At large utility-scale plants automated cleaning systems are often used. Keeping panels clean optimizes electricity generation.
How does geographic location impact solar plant productivity?
Sites with greater average annual irradiance and sunlight hours will generate more solar electricity. Deserts and equatorial regions tend to have the most solar energy potential.
What reduces output from shaded solar panels?
Even small amounts of shading from buildings, trees, or structures can significantly lower power output from affected panels. Careful site selection and placement is key to avoiding shading.
How can energy storage increase solar power production?
Storing excess daytime solar energy in batteries allows the plant to smooth production and provide power when the sun isn’t shining. Overall utilization and capacity factor increases.